Filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella bronchiseptica is required for efficient establishment of tracheal colonization
- PMID: 9826374
- PMCID: PMC108750
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5921-5929.1998
Filamentous hemagglutinin of Bordetella bronchiseptica is required for efficient establishment of tracheal colonization
Abstract
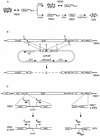
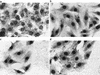
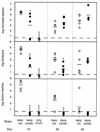
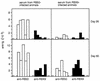
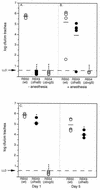
Adherence to ciliated respiratory epithelial cells is considered a critical early step in Bordetella pathogenesis. For Bordetella pertussis, the etiologic agent of whooping cough, several factors have been shown to mediate adherence to cells and cell lines in vitro. These putative adhesins include filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA), fimbriae, pertactin, and pertussis toxin. Determining the precise roles of each of these factors in vivo, however, has been difficult, due in part to the lack of natural-host animal models for use with B. pertussis. Using the closely related species Bordetella bronchiseptica, and by constructing both deletion mutation and ectopic expression mutants, we have shown that FHA is both necessary and sufficient for mediating adherence to a rat lung epithelial (L2) cell line. Using a rat model of respiratory infection, we have shown that FHA is absolutely required, but not sufficient, for tracheal colonization in healthy, unanesthetized animals. FHA was not required for initial tracheal colonization in anesthetized animals, however, suggesting that its role in establishment may be dedicated to overcoming the clearance action of the mucociliary escalator.
Figures

References
-
- Akerley B J, Cotter P A, Miller J F. Ectopic expression of the flagellar regulon alters development of the Bordetella-host interaction. Cell. 1995;80:611–620. - PubMed
-
- Boschwitz J S, Batanghari J W, Kedem H, Relman D A. Bordetella pertussis infection of human monocytes inhibits antigen-dependent CD4 T cell proliferation. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:678–686. - PubMed
-
- Brennan M J, Hannah J H, Leininger E. Adhesion of Bordetella pertussis to sulfatides and to the GalNAc beta 4Gal sequence found in glycosphingolipids. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:18827–18831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

