An essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in myogenic differentiation
- PMID: 9826674
- PMCID: PMC24347
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14179
An essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in myogenic differentiation
Abstract
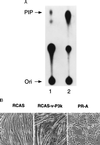
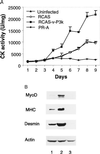
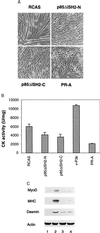
The oncogene p3k, coding for a constitutively active form of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase; EC 2.7.1.137), strongly enhances myogenic differentiation in cultures of chicken-embryo myoblasts. It increases the size of the myotubes and induces elevated levels of the muscle-specific proteins MyoD, myosin heavy chain, creatine kinase, and desmin. Inhibition of PI 3-kinase activity with LY294002 or with dominant-negative mutants of PI 3-kinase interferes with myogenic differentiation and with the induction of muscle-specific genes. PI 3-kinase is therefore an upstream mediator for the expression of the muscle-specific genes and is both necessary and rate-limiting for the process of myogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Davis R L, Weintraub H, Lassar A B. Cell. 1987;51:987–1000. - PubMed
-
- Weintraub H, Davis R, Tapscott S, Thayer M, Krause M, Benezra R, Blackwell T K, Turner D, Rupp R, Hollenberg S, et al. Science. 1991;251:761–766. - PubMed
-
- Lassar A, Munsterberg A. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994;6:432–442. - PubMed
-
- Lassar A B, Buskin J N, Lockshon D, Davis R L, Apone S, Hauschka S D, Weintraub H. Cell. 1989;58:823–831. - PubMed
-
- Molkentin J D, Olson E N. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996;6:445–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

