Endothelin ETA receptor blockade restores NO-mediated endothelial function and inhibits atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- PMID: 9826706
- PMCID: PMC24379
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14367
Endothelin ETA receptor blockade restores NO-mediated endothelial function and inhibits atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
Abstract
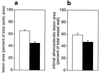
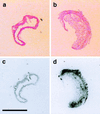
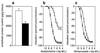
This study investigated whether endothelin-1 (ET-1), a potent vasoconstrictor, which also stimulates cell proliferation, contributes to endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Apolipoprotein E (apoE)-deficient mice and C57BL/6 control mice were treated with a Western-type diet to accelerate atherosclerosis with or without ETA receptor antagonist LU135252 (50 mg/kg/d) for 30 wk. Systolic blood pressure, plasma lipid profile, and plasma nitrate levels were determined. In the aorta, NO-mediated endothelium-dependent relaxation, atheroma formation, ET receptor-binding capacity, and vascular ET-1 protein content were assessed. In apoE-deficient but not C57BL/6 mice, severe atherosclerosis developed within 30 wk. Aortic ET-1 protein content (P < 0.0001) and binding capacity for ETA receptors was increased as compared with C57BL/6 mice. In contrast, NO-mediated, endothelium-dependent relaxation to acetylcholine (56 +/- 3 vs. 99 +/- 2%, P < 0.0001) and plasma nitrate were reduced (57.9 +/- 4 vs. 93 +/- 10 micromol/liter, P < 0.01). Treatment with the ETA receptor antagonist LU135252 for 30 wk had no effect on the lipid profile or systolic blood pressure in apoE-deficient mice, but increased NO-mediated endothelium-dependent relaxation (from 56 +/- 3 to 93 +/- 2%, P < 0.0001 vs. untreated) as well as circulating nitrate levels (from 57.9 +/- 4 to 80 +/- 8.3 micromol/liter, P < 0.05). Chronic ETA receptor blockade reduced elevated tissue ET-1 levels comparable with those found in C57BL/6 mice and inhibited atherosclerosis in the aorta by 31% without affecting plaque morphology or ET receptor-binding capacity. Thus, chronic ETA receptor blockade normalizes NO-mediated endothelial dysfunction and reduces atheroma formation independent of plasma cholesterol and blood pressure in a mouse model of human atherosclerosis. ETA receptor blockade may have therapeutic potential in patients with atherosclerosis.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

