Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo
- PMID: 9826710
- PMCID: PMC24383
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14389
Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo
Abstract
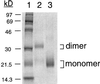
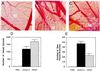
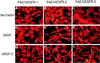
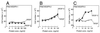
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) recently has been described to be a relatively specific growth factor for the lymphatic vascular system. Here we report that ectopic application of recombinant VEGF-C also has potent angiogenic effects in vivo. VEGF-C is sufficiently potent to stimulate neovascularization from limbal vessels in the mouse cornea. Similar to VEGF, the angiogenic response of corneas induced by VEGF-C is intensive, with a high density of new capillaries. However, the outgrowth of microvessels stimulated by VEGF-C was significantly longer than that induced by VEGF. In the developing embryo, VEGF-C was able to induce branch sprouts from the established blood vessels. VEGF-C also induced an elongated, spindle-like cell shape change and actin reorganization in both VEGF receptor (VEGFR)-2 and VEGFR-3-overexpressing endothelial cells, but not in VEGFR-1-expressing cells. Further, both VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 could mediate proliferative and chemotactic responses in endothelial cells on VEGF-C stimulation. Thus, VEGF-C may regulate physiological angiogenesis and participate in the development and progression of angiogenic diseases in addition to lymphangiogenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Folkman J, Shing Y. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10931–10934. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Nat Med. 1995;1:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J. Cell. 1996;86:353–364. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1757–1763. - PubMed
-
- Senger D R, Galli S J, Dvorak A M, Perruzzi C A, Harvey V S, Dvorak H F. Science. 1983;219:983–985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

