Identification and characterization of SpcU, a chaperone required for efficient secretion of the ExoU cytotoxin
- PMID: 9829931
- PMCID: PMC107707
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.23.6224-6231.1998
Identification and characterization of SpcU, a chaperone required for efficient secretion of the ExoU cytotoxin
Abstract
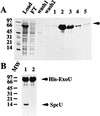
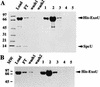
In recent studies, we have shown that Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains that are acutely cytotoxic in vitro damage the lung epithelium in vivo. Genetic analysis indicated that the factor responsible for acute cytotoxicity was controlled by ExsA and therefore was part of the exoenzyme S regulon. The specific virulence determinant responsible for epithelial damage in vivo and cytotoxicity in vitro was subsequently mapped to the exoU locus. The present studies are focused on a genetic characterization of the exoU locus. Northern blot analyses and complementation experiments indicated that a region downstream of exoU was expressed and that the expression of this region corresponded to increased ExoU secretion. DNA sequence analysis of a region downstream of exoU identified several potential coding regions. One of these open reading frames, SpcU (specific Pseudomonas chaperone for ExoU), encoded a small 15-kDa acidic protein (137 amino acids [pI 4.4]) that possessed a leucine-rich motif associated with the Syc family of cytosolic chaperones for the Yersinia Yops. T7 expression analysis and nickel chromatography of histidine-tagged proteins indicated that ExoU and SpcU associated as a noncovalent complex when coexpressed in Escherichia coli. The association of ExoU and SpcU required amino acids 3 to 123 of ExoU. In P. aeruginosa, ExoU and SpcU are coordinately expressed as an operon that is controlled at the transcriptional level by ExsA.
Figures

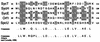




References
-
- Anderson D, Schneewind O. A mRNA signal for the type III secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. Science. 1997;278:1140–1143. - PubMed
-
- Bette-Bobillo P, Giro P, Sainte-Marie J, Vidal M. Exoenzyme S from P. aeruginosa ADP ribosylates rab4 and inhibits transferrin recycling in SLO-permeabilized reticulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;244:336–341. - PubMed
-
- Cheng L W, Anderson D M, Schneewind O. Two independent type III secretion mechanisms for YopE in Yersinia enterocolitica. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:757–765. - PubMed
-
- Cornelis G R, Wolf-Watz H. The Yersinia Yop virulon: a bacterial system for subverting eukaryotic cells. Mol Microbiol. 1997;23:861–867. - PubMed
-
- Finck-Barbançon V, Goranson J, Zhu L, Sawa T, Wiener-Kronish J P, Fleiszig S M J, Wu C, Mende-Mueller L, Frank D W. ExoU expression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa correlates with acute cytotoxicity and epithelial injury. Mol Microbiol. 1997;25:547–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

