Dorsoventral patterning in the Drosophila central nervous system: the vnd homeobox gene specifies ventral column identity
- PMID: 9832511
- PMCID: PMC317246
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.22.3603
Dorsoventral patterning in the Drosophila central nervous system: the vnd homeobox gene specifies ventral column identity
Abstract
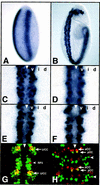
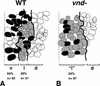
The Drosophila CNS develops from three columns of neuroectodermal cells along the dorsoventral (DV) axis: ventral, intermediate, and dorsal. In this and the accompanying paper, we investigate the role of two homeobox genes, vnd and ind, in establishing ventral and intermediate cell fates within the Drosophila CNS. During early neurogenesis, Vnd protein is restricted to ventral column neuroectoderm and neuroblasts; later it is detected in a complex pattern of neurons. We use molecular markers that distinguish ventral, intermediate, and dorsal column neuroectoderm and neuroblasts, and a cell lineage marker for selected neuroblasts, to show that loss of vnd transforms ventral into intermediate column identity and that specific ventral neuroblasts fail to form. Conversely, ectopic vnd produces an intermediate to ventral column transformation. Thus, vnd is necessary and sufficient to induce ventral fates and repress intermediate fates within the Drosophila CNS. Vertebrate homologs of vnd (Nkx2.1 and 2.2) are similarly expressed in the ventral CNS, raising the possibility that DV patterning within the CNS is evolutionarily conserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dorsoventral patterning in the Drosophila central nervous system: the intermediate neuroblasts defective homeobox gene specifies intermediate column identity.Genes Dev. 1998 Nov 15;12(22):3591-602. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.22.3591. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9832510 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and specification of ventral neuroblasts is controlled by vnd in Drosophila neurogenesis.Genes Dev. 1998 Nov 15;12(22):3613-24. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.22.3613. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9832512 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of dorsal, dpp, and egfr signaling pathways subdivides the drosophila neuroectoderm into three dorsal-ventral columns.Dev Biol. 2000 Aug 15;224(2):362-72. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9789. Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 10926773
-
Vnd/nkx, ind/gsh, and msh/msx: conserved regulators of dorsoventral neural patterning?Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000 Feb;10(1):63-71. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(99)00049-5. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10679430 Review.
-
Dorsoventral patterning of the brain: a comparative approach.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;628:42-56. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78261-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18683637 Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila Embryonic CNS Development: Neurogenesis, Gliogenesis, Cell Fate, and Differentiation.Genetics. 2019 Dec;213(4):1111-1144. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.300974. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31796551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional profiling from whole embryos to single neuroblast lineages in Drosophila.Dev Biol. 2022 Sep;489:21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2022.05.018. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35660371 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of temporal and spatial patterning generates neural diversity.Nature. 2017 Jan 19;541(7637):365-370. doi: 10.1038/nature20794. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28077877 Free PMC article.
-
EvoD/Vo: the origins of BMP signalling in the neuroectoderm.Nat Rev Genet. 2008 Sep;9(9):663-77. doi: 10.1038/nrg2417. Nat Rev Genet. 2008. PMID: 18679435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Huckebein-mediated autoregulation of Glide/Gcm triggers glia specification.EMBO J. 2006 Jan 11;25(1):244-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600907. Epub 2005 Dec 15. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16362045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhat KM. The patched signaling pathway mediates repression of gooseberry allowing neuroblast specification by wingless during Drosophila neurogenesis. Development. 1996;122:921–932. - PubMed
-
- Bhat KM, Schedl P. Requirement for engrailed and invected genes reveals novel regulatory interactions between engrailed/invected, patched, gooseberry and wingless during Drosophila neurogenesis. Development. 1997;124:1675–1688. - PubMed
-
- Bier E. Anti-neural inhibition: A conserved mechanism for neural induction. Cell. 1997;89:681–684. - PubMed
-
- Broadus J, Skeath JB, Spana EP, Bossing T, Technau G, Doe CQ. New neuroblast markers and the origin of the aCC/pCC neurons in the Drosophila central nervous system. Mech Dev. 1995;53:393–402. - PubMed
-
- Buescher M, Chia W. Mutations in lottchen cause cell fate transformations in both neuroblast and glioblast lineages in the Drosophila embryonic central nervous system. Development. 1997;124:673–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
