Human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors serve as substrates for multidrug transporter proteins MDR1 and MRP1 but retain antiviral efficacy in cell lines expressing these transporters
- PMID: 9835508
- PMCID: PMC106016
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.12.3157
Human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors serve as substrates for multidrug transporter proteins MDR1 and MRP1 but retain antiviral efficacy in cell lines expressing these transporters
Abstract
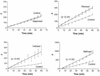
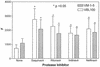
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) protease inhibitors (PIs)-saquinavir, ritonavir, nelfinavir, and indinavir-interact with the ABC-type multidrug transporter proteins MDR1 and MRP1 in CEM T-lymphocytic cell lines. Calcein fluorescence was significantly enhanced in MDR1(+) CEM/VBL100 and MRP1(+) CEM/VM-1-5 cells incubated in the presence of various HIV PIs and calcein acetoxymethyl ester. HIV PIs also enhanced the cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin, a known substrate for MDR1 and MRP1, in both VBL100 and VM-1-5 CEM lines. Saquinavir, ritonavir, and nelfinavir enhanced doxorubicin toxicity in CEM/VBL100 cells by approximately three- to sevenfold. Saquinavir and ritonavir also enhanced doxorubicin toxicity in CEM/VM-1-5 cells. HIV-1 replication was effectively inhibited by the various PIs in all of the cell lines, and the 90% inhibitory concentration for a given compound was comparable between the different cell types. Therefore, overexpression of MDR1 or MRP1 by T lymphocytes is not likely to limit the antiviral efficacy of HIV PI therapy.
Figures


Comment in
-
May the drug transporter P glycoprotein affect the antiviral activity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 proteinase inhibitors?Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000 Feb;44(2):473-4. doi: 10.1128/AAC.44.2.473-474.2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000. PMID: 10733463 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alsenz J, Steffen H, Alex R. Active apical secretory efflux of the HIV protease inhibitors saquinavir and ritonavir in caco-2 cell monolayers. Pharm Res. 1998;15:423–428. - PubMed
-
- Andreana A, Aggarwal S, Gollapudi S, Wien D, Tsuruo T, Gupta S. Abnormal expression of a 170 kilodalton P-glycoprotein encoded by MDR1 gene, a metabolically active efflux pump, in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from patients with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1996;12:1457–1462. - PubMed
-
- Barry M, Gibbons S, Back D, Mulcahy F. Protease inhibitors in patients with HIV disease. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997;32:194–209. - PubMed
-
- Beck W T. Vinca alkaloid-resistant phenotype in cultured human leukemic lymphoblasts. Cancer Treat Rep. 1983;67:875–882. - PubMed
-
- Beck W T, Cirtain M C. Continued expression of vinca alkaloid resistance by CCRF-CEM cells after treatment with tunicamycin or pronase. Cancer Res. 1982;42:184–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

