Serum and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral lamivudine in human immunodeficiency virus-infected children
- PMID: 9835513
- PMCID: PMC106021
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.12.3187
Serum and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral lamivudine in human immunodeficiency virus-infected children
Abstract
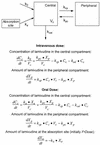
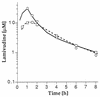
We studied the pharmacokinetics of intravenously and orally administered lamivudine at six dose levels ranging from 0.5 to 10 mg/kg of body weight in 52 children with human immunodeficiency virus infection. A two-compartment model with first-order elimination from the central compartment was simultaneously fitted to the serum drug concentration-time data obtained after intravenous and oral administration. The maximal concentration at the end of the 1-h intravenous infusion and the area under the concentration-time curve after oral and intravenous administration increased proportionally with the dose. The mean clearance of lamivudine (+/- standard deviation) in the children was 0.53 +/- 0.19 liter/kg/h (229 +/- 77 ml/min/m2 of body surface area), and the mean half-lives at the distribution and elimination phases were 0.23 +/- 0.18 and 2.2 +/- 2.1 h, respectively. Clearance was age dependent when normalized to body weight but age independent when normalized to body surface area. Lamivudine was rapidly absorbed after oral administration, and 66% +/- 25% of the oral dose was absorbed. Serum lamivudine concentrations were maintained above 1 microM for >/=8 h of 24 h on the twice daily oral dosing schedule with doses of >/=2 mg/kg. The cerebrospinal fluid drug concentration measured 2 to 4 h after the dose was 12% (range, 0 to 46%) of the simultaneously measured serum drug concentration. A limited-sampling strategy was developed to estimate the area under the concentration-time curve for concentrations in serum at 2 and 6 h.
Figures
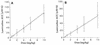
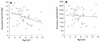
References
-
- Angel J B, Hussey E K, Hall S T, Donn K H, Morris D M, McCormack J P, Montaner J S G, Ruedy J. Pharmacokinetics of 3TC (GR109714X) administered with and without food to HIV-infected patients. Drug Investig. 1993;6:70–74.
-
- Balis F M, Pizzo P A, Butler K M, Hawkins M E, Brouwers P, Husson R N, Jacobsen F, Blaney S M, Gress J, Jarosinski P, Poplack D G. Clinical pharmacology of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine in human immunodeficiency virus-infected children. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:99–104. - PubMed
-
- Balis F M, Pizzo P A, Eddy J, Wilfert C, McKinney R, Scott G, Murphy R F, Jarosinski P F, Falloon J, Poplack D G. Pharmacokinetics of zidovudine administered intravenously and orally in children with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Pediatr. 1989;114:880–884. - PubMed
-
- Cammack N, Rouse P, Marr C L, Reid P J, Boehme R E, Coates J A, Penn C R, Cameron J M. Cellular metabolism of (−) enantiomeric 2′-deoxy-3′-thiacytidine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;43:2059–2064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

