Efficacy of the carbocyclic 2'-deoxyguanosine nucleoside BMS-200475 in the woodchuck model of hepatitis B virus infection
- PMID: 9835516
- PMCID: PMC106024
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.12.3209
Efficacy of the carbocyclic 2'-deoxyguanosine nucleoside BMS-200475 in the woodchuck model of hepatitis B virus infection
Erratum in
- Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1999 Mar;43(3):726
Abstract
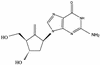
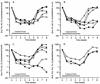
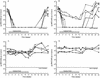
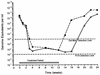
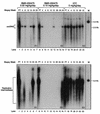
Daily oral treatment with the cyclopentyl 2'-deoxyguanosine nucleoside BMS-200475 at doses ranging from 0.02 to 0.5 mg/kg of body weight for 1 to 3 months effectively reduced the level of woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) viremia in chronically infected woodchucks as measured by reductions in serum WHV DNA levels and endogenous hepadnaviral polymerase activity. Within 4 weeks of daily therapy with 0.5 or 0.1 mg of BMS-200475 per kg, endogenous viral polymerase levels in serum were reduced about 1,000-fold compared to pretreatment levels. Serum WHV DNA levels determined by a dot blot hybridization technique were comparably decreased in these treated animals. In the 3-month study, the sera of animals that had undetectable levels of WHV DNA by the dot blot technique were further analyzed by a highly sensitive semiquantitative PCR assay. The results indicate that BMS-200475 therapy reduced mean WHV titers by 10(7)- to 10(8)-fold, down to levels as low as 10(2) to 10(3) virions/ml of serum. Southern blot hybridization analysis of liver biopsy samples taken from animals during and after BMS-200475 treatment showed remarkable reductions in the levels of WHV DNA replicative intermediates and in the levels of covalently closed circular viral DNA. WHV viremia in BMS-200475-treated WHV carriers eventually returned to pretreatment levels after therapy was stopped. These results indicate that BMS-200475 should be evaluated in clinical trials for the therapy of chronic human hepatitis B virus infections.
Figures
References
-
- Bacon T H. Famciclovir, from the bench to the patient—a comprehensive review of preclinical data. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1996;7:119–134. - PubMed
-
- Bartholomeusz A, Locarnini S. Mutations in the hepatitis B virus polymerase gene that are associated with resistance to famciclovir and lamivudine. Int Antivir News. 1997;5:123–124.
-
- Bartholomew M M, Jansen R W, Jeffers L J, Reddy K R, Johnson L C, Bunzendahl H, Condreay L D, Tzakis A G, Schiff E R, Brown N A. Hepatitis-B-virus resistance to lamivudine given for recurrent infection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Lancet. 1997;349:20–22. - PubMed
-
- Beasley R P, Hwang L Y. Overview on the epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Hollinger F B, Lemon S M, Margolis M, editors. Viral hepatitis and liver disease. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1991. pp. 532–535.
-
- Bisacchi G S, Chao S T, Bachard C, Daris J P, Innaimo S F, Jacobs J A, Kocy O, Lapointe P, Martel A, Merchant Z, Slusarchyk W A, Sundeen J E, Young M G, Colonno R J, Zahler R. BMS-200475, a novel carbocyclic 2′-deoxyguanosine analog with potent and selective anti-hepatitis B virus activity in vitro. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1997;7:127–132.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

