The oxazolidinone linezolid inhibits initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria
- PMID: 9835522
- PMCID: PMC106030
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.12.3251
The oxazolidinone linezolid inhibits initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria
Abstract
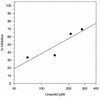
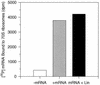
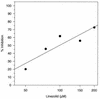
The oxazolidinones represent a new class of antimicrobial agents which are active against multidrug-resistant staphylococci, streptococci, and enterococci. Previous studies have demonstrated that oxazolidinones inhibit bacterial translation in vitro at a step preceding elongation but after the charging of N-formylmethionine to the initiator tRNA molecule. The event that occurs between these two steps is termed initiation. Initiation of protein synthesis requires the simultaneous presence of N-formylmethionine-tRNA, the 30S ribosomal subunit, mRNA, GTP, and the initiation factors IF1, IF2, and IF3. An initiation complex assay measuring the binding of [3H]N-formylmethionyl-tRNA to ribosomes in response to mRNA binding was used in order to investigate the mechanism of oxazolidinone action. Linezolid inhibited initiation complex formation with either the 30S or the 70S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. In addition, complex formation with Staphylococcus aureus 70S tight-couple ribosomes was inhibited by linezolid. Linezolid did not inhibit the independent binding of either mRNA or N-formylmethionyl-tRNA to E. coli 30S ribosomal subunits, nor did it prevent the formation of the IF2-N-formylmethionyl-tRNA binary complex. The results demonstrate that oxazolidinones inhibit the formation of the initiation complex in bacterial translation systems by preventing formation of the N-formylmethionyl-tRNA-ribosome-mRNA ternary complex.
Figures

References
-
- Brickner S J, Hutchinson D K, Barbachyn M R, Manninen P R, Ulanowicz D A, Garmon S A, Grega K C, Hendges S K, Toops D S, Zurenko G E, Ford C W. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of U-100592 and U-100766, two oxazolidinone antibacterial agents for the potential treatment of multidrug-resistant gram-positive bacterial infections. J Med Chem. 1996;39:673–679. - PubMed
-
- Burghardt H, Schimz K L, Muller M. On the target of a novel class of antibiotics, oxazolidinones, active against multidrug-resistant gram-positive bacteria. FEBS Lett. 1998;425:40–44. - PubMed
-
- Buysse J M, Demyan W F, Dunyak D S, Stapert D, Hamel J C, Ford C W. Program and abstracts of the 36th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1996. Mutation of the AcrAB antibiotic efflux pump in Escherichia coli confers susceptibility to oxazolidinone antibiotics, abstr. C-42; p. 41.
-
- Eustice D C, Feldman P A, Slee A M. Mechanism of action of DuP 721, a new antibacterial agent: effects on macromolecular synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;150:965–971. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

