The effect of multiple doses of donepezil HCl on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of warfarin
- PMID: 9839766
- PMCID: PMC1873807
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.0460s1045.x
The effect of multiple doses of donepezil HCl on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of warfarin
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the study was to examine the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of single doses of warfarin (25 mg) following administration alone, and in combination with multiple doses of donepezil HCl (10 mg day(-1)) in healthy volunteers.
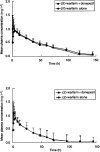
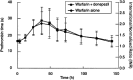
Methods: This was an open-label, two-period crossover study in 12 healthy male volunteers, aged 18-55 years, who were randomized to one of the following treatment groups: (A) donepezil administered for 19 consecutive days with a single dose of warfarin administered on day 14. On day 20, there was a 21-day washout period after which a single dose of warfarin was again administered, and (B) an initial 13-day period with no medication, then a single dose of warfarin administered alone on day 14, followed by a 14-day washout period. Donepezil was then administered for 19 days (to day 47), with an additional single dose of warfarin administered on day 41. Serial blood samples were collected over 144 h following both warfarin administrations in each treatment group. Pharmacokinetic parameters were assessed for both (R)- and (S)-warfarin concentrations in plasma, and pharmacodynamic analyses utilizing prothrombin time were undertaken. Warfarin concentrations in plasma were determined by HPLC with fluorescence detection. The pharmacokinetic parameters Cmax, AUC(0-infinity), CL(T)/F, Vlambdaz/F and t1/2 of both (R)- and (S)-warfarin, maximum prothrombin time (Rmax) and the area under the prothrombin-time curve (AUC(PT)), were compared in the presence and absence of donepezil by analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Results: No statistically significant differences in (R)- or (S)-warfarin pharmacokinetics were observed when warfarin administered alone was compared to warfarin administered concurrently with donepezil. Warfarin pharmacodynamic parameters, Rmax and AUC(PT), were also unchanged by concomitant administration ofdonepezil. No clinically significant changes in vital signs, ECG parameters or clinical laboratory tests were observed.
Conclusions: Concurrent administration of donepezil HCl does not alter the pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic profile of single doses of warfarin in healthy volunteers. These findings suggest that donepezil may be safely co-administered with warfarin without the need for dose modification.
Figures
References
-
- Iimura Y, Mishima M, Sugimoto H. Synthesis of 1-benzyl-4-lsqb;(5,6-dimethoxylsqb;2−14C]-1-indanon)-2-yl]-methylpiperidine hydrochloride (E2020–14C) J Label Compounds Radiopharm. 1989;XXVII:835–839.
-
- Rogers SL, Yamanishi Y, Yamatsu K. E2020—the pharmacology of a piperidine cholinesterase inhibitor. In: Becker R, Giacobini E, editors. Cholinergic Basis for Alzheimer Therapy. Boston: Birkhäuser; 1991. pp. 314–320.
-
- Sherman K. Pharmacodynamics of oral E2020 and tacrine in humans: novel approaches. In: Becker R, Giacobini E, editors. Cholinergic Basis for Alzheimer Therapy. Boston: Birkhäuser; 1991. pp. 321–328.
-
- Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT the Donepezil Study Group. The efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: results of a US multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Dementia. 1996;7:293–303. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SL, Farlow MR, Doody RS, Mohs R, Friedhoff LT the Donepezil Study Group. A 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1998;50:136–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

