TGF-beta-induced phosphorylation of Smad3 regulates its interaction with coactivator p300/CREB-binding protein
- PMID: 9843571
- PMCID: PMC25628
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.12.3309
TGF-beta-induced phosphorylation of Smad3 regulates its interaction with coactivator p300/CREB-binding protein
Abstract
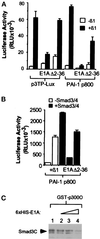
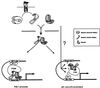
Smads are intermediate effector proteins that transduce the TGF-beta signal from the plasma membrane to the nucleus, where they participate in transactivation of downstream target genes. We have shown previously that coactivators p300/CREB-binding protein are involved in TGF-beta-mediated transactivation of two Cdk inhibitor genes, p21 and p15. Here we examined the possibility that Smads function to regulate transcription by directly interacting with p300/CREB-binding protein. We show that Smad3 can interact with a C-terminal fragment of p300 in a temporal and phosphorylation-dependent manner. TGF-beta-mediated phosphorylation of Smad3 potentiates the association between Smad3 and p300, likely because of an induced conformational change that removes the autoinhibitory interaction between the N- and C-terminal domains of Smad3. Consistent with a role for p300 in the transcription regulation of multiple genes, overexpression of a Smad3 C-terminal fragment causes a general squelching effect on multiple TGF-beta-responsive reporter constructs. The adenoviral oncoprotein E1A can partially block Smad-dependent transcriptional activation by directly competing for binding to p300. Taken together, these findings define a new role for phosphorylation of Smad3: in addition to facilitating complex formation with Smad4 and promoting nuclear translocation, the phosphorylation-induced conformational change of Smad3 modulates its interaction with coactivators, leading to transcriptional regulation.
Figures


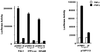
References
-
- Arias J, Alberts AS, Brindle P, Claret FX, Smeal T, Karin M, Feramisco J, Montminy M. Activation of cAMP and mitogen responsive genes relies on a common nuclear factor. Nature. 1994;370:226–229. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Harland R. A novel mesoderm inducer, Madr2, functions in the activin signal transduction pathway. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1880–1889. - PubMed
-
- Barrett MT, Schutte M, Kern SE, Reid BJ. Allelic loss and mutational analysis of the DPC4 gene in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4351–4353. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya S, Eckner R, Grossman S, Oldread E, Arany Z, D’Andrea A, Livingston DM. Cooperation of Stat2 and p300/CBP in signaling by interferon. Nature. 1996;383:344–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

