Nck-2, a novel Src homology2/3-containing adaptor protein that interacts with the LIM-only protein PINCH and components of growth factor receptor kinase-signaling pathways
- PMID: 9843575
- PMCID: PMC25640
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.9.12.3367
Nck-2, a novel Src homology2/3-containing adaptor protein that interacts with the LIM-only protein PINCH and components of growth factor receptor kinase-signaling pathways
Abstract
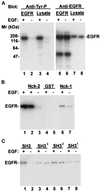
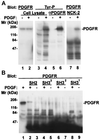
Many of the protein-protein interactions that are essential for eukaryotic intracellular signal transduction are mediated by protein binding modules including SH2, SH3, and LIM domains. Nck is a SH3- and SH2-containing adaptor protein implicated in coordinating various signaling pathways, including those of growth factor receptors and cell adhesion receptors. We report here the identification, cloning, and characterization of a widely expressed, Nck-related adaptor protein termed Nck-2. Nck-2 comprises primarily three N-terminal SH3 domains and one C-terminal SH2 domain. We show that Nck-2 interacts with PINCH, a LIM-only protein implicated in integrin-linked kinase signaling. The PINCH-Nck-2 interaction is mediated by the fourth LIM domain of PINCH and the third SH3 domain of Nck-2. Furthermore, we show that Nck-2 is capable of recognizing several key components of growth factor receptor kinase-signaling pathways including EGF receptors, PDGF receptor-beta, and IRS-1. The association of Nck-2 with EGF receptors was regulated by EGF stimulation and involved largely the SH2 domain of Nck-2, although the SH3 domains of Nck-2 also contributed to the complex formation. The association of Nck-2 with PDGF receptor-beta was dependent on PDGF activation and was mediated solely by the SH2 domain of Nck-2. Additionally, we have detected a stable association between Nck-2 and IRS-1 that was mediated primarily via the second and third SH3 domain of Nck-2. Thus, Nck-2 associates with PINCH and components of different growth factor receptor-signaling pathways via distinct mechanisms. Finally, we provide evidence indicating that a fraction of the Nck-2 and/or Nck-1 proteins are associated with the cytoskeleton. These results identify a novel Nck-related SH2- and SH3-domain-containing protein and suggest that it may function as an adaptor protein connecting the growth factor receptor-signaling pathways with the integrin-signaling pathways.
Figures




References
-
- Anton IM, Lu W, Mayer BJ, Ramesh N, Geha RS. The Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein-interacting Protein (WIP) binds to the adaptor protein Nck. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:20992–20995. - PubMed
-
- Bartfeld NS, Pasquale EB, Geltosky JE, Languino LR. The alpha v beta 3 integrin associates with a 190-kDa protein that is phosphorylated on tyrosine in response to platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:17270–17276. - PubMed
-
- Birge RB, Knudsen BS, Besser D, Hanafusa H. SH2 and SH3-containing adaptor proteins: redundant or independent mediators of intracellular signal transduction. Genes Cells. 1996;1:595–613. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch GM, Wang Y, Bohl BP, Sells MA, Quilliam LA, Knaus UG. Interaction of the Nck adapter protein with p21-activated kinase (PAK1) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:25746–25749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

