Genome scan of human systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for linkage on chromosome 1q in African-American pedigrees
- PMID: 9843982
- PMCID: PMC24542
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.25.14869
Genome scan of human systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for linkage on chromosome 1q in African-American pedigrees
Abstract
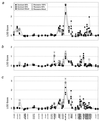
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by production of autoantibodies against intracellular antigens including DNA, ribosomal P, Ro (SS-A), La (SS-B), and the spliceosome. Etiology is suspected to involve genetic and environmental factors. Evidence of genetic involvement includes: associations with HLA-DR3, HLA-DR2, Fcgamma receptors (FcgammaR) IIA and IIIA, and hereditary complement component deficiencies, as well as familial aggregation, monozygotic twin concordance >20%, lambdas > 10, purported linkage at 1q41-42, and inbred mouse strains that consistently develop lupus. We have completed a genome scan in 94 extended multiplex pedigrees by using model-based linkage analysis. Potential [log10 of the odds for linkage (lod) > 2.0] SLE loci have been identified at chromosomes 1q41, 1q23, and 11q14-23 in African-Americans; 14q11, 4p15, 11q25, 2q32, 19q13, 6q26-27, and 12p12-11 in European-Americans; and 1q23, 13q32, 20q13, and 1q31 in all pedigrees combined. An effect for the FcgammaRIIA candidate polymorphism) at 1q23 (lod = 3.37 in African-Americans) is syntenic with linkage in a murine model of lupus. Sib-pair and multipoint nonparametric analyses also support linkage (P < 0.05) at nine loci detected by using two-point lod score analysis (lod > 2.0). Our results are consistent with the presumed complexity of genetic susceptibility to SLE and illustrate racial origin is likely to influence the specific nature of these genetic effects.
Figures

References
-
- Hochberg M C. In: Dubois’ Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. 5th Ed. Wallace D J, Hahn B J, editors. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1997. pp. 49–65.
-
- Arnett F C. In: Dubois’ Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. 5th Ed. Wallace D J, Hahn B J, editors. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1997. pp. 77–117.
-
- Duits A J, Bootsma H, Derksen R H, Spronk P E, Kater L, Kallenberg C G, Capel P J, Westerdaal N A, Spierenburg G T, Gmelig-Meyling F H, van de Winkel J G. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1832–1836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

