Inhibition of proximal convoluted tubule transport by dopamine
- PMID: 9844135
- PMCID: PMC4103744
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00156.x
Inhibition of proximal convoluted tubule transport by dopamine
Abstract
Background: Dopamine can produce a natriuresis and diuresis independent of changes in renal hemodynamics. However, previous studies have failed to demonstrate an inhibition of transport by dopamine in intact proximal convoluted tubules.
Methods: Rabbit proximal convoluted tubules were perfused in vitro with an ultrafiltrate-like solution and bathed in a serum-like albumin solution.
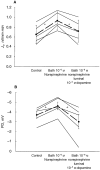
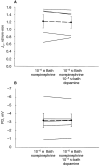
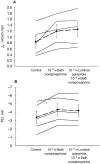
Results: In the present study, the addition of 10-5 M dopamine to the lumen or bath of proximal convoluted tubules perfused in vitro had no effect on transport. In proximal convoluted tubules, addition of 10-6 M bath norepinephrine increased the rate of volume absorption from 0.65 +/- 0.08 to 0.93 +/- 0.08 nl/mm. min (P < 0.01). Addition of 10-5 M luminal dopamine in the presence of bath norepinephrine inhibited the rate of volume absorption to 0.72 +/- 0.10 nl/mm. min (P = 0.01). The inhibition in the rate of volume absorption by luminal dopamine in the presence of bath norepinephrine was completely blocked by the DA1 antagonist, SCH 23390. The DA1 agonist luminal 10-5 M fenoldopam also inhibited volume absorption in the presence of bath norepinephrine, but the DA2 agonist luminal 10-5 M quinpirole was without effect. Bath 10-5 M dopamine had no effect on volume absorption in the presence of bath norepinephrine.
Conclusion: Dopamine has no direct epithelial action on the proximal convoluted tubule. However, luminal dopamine antagonizes the stimulation in transport produced by norepinephrine. These studies suggest that luminal dopamine may play a role to modulate sodium transport in the presence of renal nerve activity.
Figures



References
-
- CAREY, RM, VAN LOON GR, BAINES AD, ORTT EM. Decreased plasma and urinary dopamine during dietary sodium depletion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981;52:903–909. - PubMed
-
- OATES NS, BALL SG, PERKINS CM, LEE MR. Plasma and urine dopamine in man given sodium chloride in the diet. Clin Sci. 1979;56:261–264. - PubMed
-
- LOKHANDWALA MF, VYAS SJ, HEGDE SS. Renal dopamine and tubular DA-1 receptors in the regulation of sodium excretion. J Auton Pharmacol. 1990;10(Suppl 1):S31–S39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

