Expression of beta-amylase from alfalfa taproots
- PMID: 9847126
- PMCID: PMC34768
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.118.4.1495
Expression of beta-amylase from alfalfa taproots
Abstract
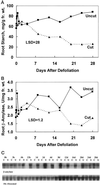
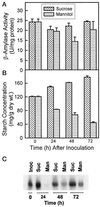
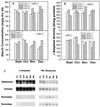
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) roots contain large quantities of beta-amylase, but little is known about its role in vivo. We studied this by isolating a beta-amylase cDNA and by examining signals that affect its expression. The beta-amylase cDNA encoded a 55.95-kD polypeptide with a deduced amino acid sequence showing high similarity to other plant beta-amylases. Starch concentrations, beta-amylase activities, and beta-amylase mRNA levels were measured in roots of alfalfa after defoliation, in suspension-cultured cells incubated in sucrose-rich or -deprived media, and in roots of cold-acclimated germ plasms. Starch levels, beta-amylase activities, and beta-amylase transcripts were reduced significantly in roots of defoliated plants and in sucrose-deprived cell cultures. beta-Amylase transcript was high in roots of intact plants but could not be detected 2 to 8 d after defoliation. beta-Amylase transcript levels increased in roots between September and October and then declined 10-fold in November and December after shoots were killed by frost. Alfalfa roots contain greater beta-amylase transcript levels compared with roots of sweetclover (Melilotus officinalis L.), red clover (Trifolium pratense L.), and birdsfoot trefoil (Lotus corniculatus L.). Southern analysis indicated that beta-amylase is present as a multigene family in alfalfa. Our results show no clear association between beta-amylase activity or transcript abundance and starch hydrolysis in alfalfa roots. The great abundance of beta-amylase and its unexpected patterns of gene expression and protein accumulation support our current belief that this protein serves a storage function in roots of this perennial species.
Figures

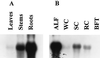
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Avice J-C, Ourry A, Volenec JJ, Lemaire G, Boucard J. Defoliation-induced changes in abundance and immuno-localization of vegetative storage proteins in taproots of Medicago sativa. Plant Physiol Biochem. 1996;34:1–11.
-
- Barber LD, Joern BC, Volenec JJ, Cunningham SM. Supplemental nitrogen effects on alfalfa regrowth and taproot nitrogen mobilization. Crop Sci. 1996;36:1217–1223.
-
- Beck E, Ziegler P. Biosynthesis and degradation of starch in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1989;40:95–117.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

