RNase L inhibitor is induced during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and down regulates the 2-5A/RNase L pathway in human T cells
- PMID: 9847332
- PMCID: PMC103833
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.290-296.1999
RNase L inhibitor is induced during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and down regulates the 2-5A/RNase L pathway in human T cells
Abstract
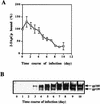
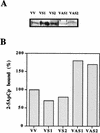
The interferon-regulated 2-5A/RNase L pathway plays a major role in the antiviral and antiproliferative activities of these cytokines. Several viruses, however, have evolved strategies to escape the antiviral activity of the 2-5A/RNase L pathway. In this context, we have cloned a cDNA coding for the RNase L inhibitor (RLI), a protein that specifically inhibits RNase L and whose regulated expression in picornavirus-infected cells down regulates the activity of the 2-5A/RNase L pathway. We show here that RLI increases during the course of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection, which may be related to the downregulation of RNase L activity that has been described to occur in HIV-infected cells. In order to establish a possible causal relationship between these observations, we have stably transfected H9 cells with RLI sense or antisense cDNA-expressing vectors. The overexpression of RLI causes a decrease in RNase L activity and a twofold enhancement of HIV production. This increase in HIV replication correlates with an increase in HIV RNA and proteins. In contrast, reduction of RLI levels in RLI antisense cDNA-expressing clones reverses the inhibition of RNase L activity associated with HIV multiplication and leads to a threefold decrease in the viral load. This anti-HIV activity correlated with a decrease in HIV RNA and proteins. These findings demonstrate that the level of RLI, via its modulation of RNase L activity, can severely impair HIV replication and suggest the involvement of RLI in the inhibition of the 2-5A/RNase L system observed during HIV infection.
Figures




References
-
- Baron S, Coppenhaver D, Dianzani F, Fleischmann W, Hughes T, Klimpel G, Niesel D, Stanton G, Tyring S. Cell effects of IFNs and animal studies. In: Baron S, editor. Interferon: principles and medical applications. Galveston, Tex: The University of Texas; 1992. pp. 271–287.
-
- Bayard B, Bisbal C, Lebleu B. Activation of ribonuclease L by (2′-5′)(A)4-poly(l-lysine) conjugates in intact cells. Biochemistry. 1986;25:3730–3736. - PubMed
-
- Bisbal C, Martinand C, Silhol M, Lebleu B, Salehzada T. Cloning and characterization of a RNase L inhibitor. A new component of the interferon-regulated 2-5A pathway. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:13308–13317. - PubMed
-
- Bisbal C, Salehzada T, Lebleu B, Bayard B. Characterization of two murine (2′-5′)(A)n-dependent endonucleases of different molecular mass. Eur J Biochem. 1989;179:595–602. - PubMed
-
- Carter W A, Strayer D R, Brodsky I, Lewin M, Pellegrino M G, Einck L, Henriques H F, Simon G L, Parenti D M, Scheib R G, et al. Clinical, immunological, and virological effects of ampligen, a mismatched double-stranded RNA, in patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Lancet. 1987;i:1286–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

