Intracellular traffic of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gE: characterization of the sorting signals required for its trans-Golgi network localization
- PMID: 9847342
- PMCID: PMC103843
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.377-387.1999
Intracellular traffic of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gE: characterization of the sorting signals required for its trans-Golgi network localization
Abstract
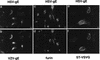
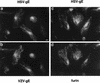
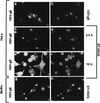
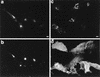
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella-zoster virus (VZV) are two pathogenic human alphaherpesviruses whose intracellular assembly is thought to follow different pathways. VZV presumably acquires its envelope in the trans-Golgi network (TGN), and it has recently been shown that its major envelope glycoprotein, VZV-gE, accumulates in this compartment when expressed alone. In contrast, the envelopment of HSV has been proposed to occur at the inner nuclear membrane, although to which compartment the gE homolog (HSV-gE) is transported is unknown. For this reason, we have studied the intracellular traffic of HSV-gE and have found that this glycoprotein accumulates at steady state in the TGN, both when expressed from cloned cDNA and in HSV-infected cells. In addition, HSV-gE cycles between the TGN and the cell surface and requires a conserved tyrosine-containing motif within its cytoplasmic tail for proper trafficking. These results show that VZV-gE and HSV-gE have similar intracellular trafficking pathways, probably reflecting the presence of similar sorting signals in the cytoplasmic domains of both molecules, and suggest that the respective viruses, VZV and HSV, could use the same subcellular organelle, the TGN, for their envelopment.
Figures

References
-
- Alconada A, Bauer U, Baudoux L, Piette J, Hoflack B. Intracellular transport of the glycoproteins gE and gI of the varicella-zoster virus: gE accelerates the maturation of gI and determines its accumulation in the trans-Golgi network. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:13430–13436. - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Dubin G, Basu M, Nguyen V, Friedman H M. Characterization of regions of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein E involved in binding the Fc domain of monomeric IgG and in forming a complex with glycoprotein I. J Immunol. 1995;154:260–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

