Nuclear events in ethylene signaling: a transcriptional cascade mediated by ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 and ETHYLENE-RESPONSE-FACTOR1
- PMID: 9851977
- PMCID: PMC317251
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.23.3703
Nuclear events in ethylene signaling: a transcriptional cascade mediated by ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 and ETHYLENE-RESPONSE-FACTOR1
Abstract
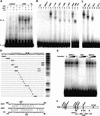
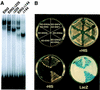
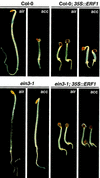
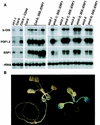
Response to the gaseous plant hormone ethylene in Arabidopsis requires the EIN3/EIL family of nuclear proteins. The biochemical function(s) of EIN3/EIL proteins, however, has remained unknown. In this study, we show that EIN3 and EILs comprise a family of novel sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins that regulate gene expression by binding directly to a primary ethylene response element (PERE) related to the tomato E4-element. Moreover, we identified an immediate target of EIN3, ETHYLENE-RESPONSE-FACTOR1 (ERF1), which contains this element in its promoter. EIN3 is necessary and sufficient for ERF1 expression, and, like EIN3-overexpression in transgenic plants, constitutive expression of ERF1 results in the activation of a variety of ethylene response genes and phenotypes. Evidence is also provided that ERF1 acts downstream of EIN3 and all other components of the ethylene signaling pathway. The results demonstrate that the nuclear proteins EIN3 and ERF1 act sequentially in a cascade of transcriptional regulation initiated by ethylene gas.
Figures




References
-
- Abeles F, Morgan P, Saltveit M. Ethylene in plant biology. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 1992.
-
- Allada R, White NE, Venus So W, Hall JC, Rosbash M. A mutant Drosophila homolog of mammalian Clock disrupts circadian rhythms and transcription of period and timeless. Cell. 1998;93:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe DC, Saunders GR, Bevan MW, Mayo MA, Harrison BD. Expression of biologically active viral satellite RNA from the nuclear genome of transformed plants. Nature. 1989;321:446–449.
-
- Bechtold N, Ellis J, Pelletier G. In Planta Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis plants. CR Acad Sci Paris Life Sci. 1993;316:1194–1199.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
