The bHLH protein PTF1-p48 is essential for the formation of the exocrine and the correct spatial organization of the endocrine pancreas
- PMID: 9851981
- PMCID: PMC317250
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.23.3752
The bHLH protein PTF1-p48 is essential for the formation of the exocrine and the correct spatial organization of the endocrine pancreas
Abstract
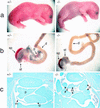
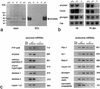
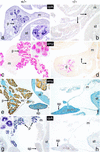
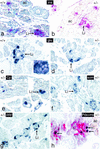
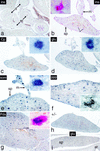
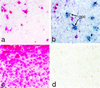
We have generated a mouse bearing a null allele of the gene encoding basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein p48, the cell-specific DNA-binding subunit of hetero-oligomeric transcription factor PTF1 that directs the expression of genes in the exocrine pancreas. The null mutation, which establishes a lethal condition shortly after birth, leads to a complete absence of exocrine pancreatic tissue and its specific products, indicating that p48 is required for differentiation and/or proliferation of the exocrine cell lineage. p48 is so far the only developmental regulator known to be required exclusively for committing cells to an exocrine fate. The hormone secreting cells of all four endocrine lineages are present in the mesentery that normally harbors the pancreatic organ until day 16 of gestation. Toward the end of embryonic life, cells expressing endocrine functions are no longer detected at their original location but are now found to colonize the spleen, where they persist in a functional state until postnatal death of the organism occurs. These findings suggest that the presence of the exocrine pancreas is required for the correct spatial assembly of the endocrine pancreas and that, in its absence, endocrine cells are directed by default to the spleen, a site that, in some reptiles, harbors part of this particular cellular compartment.
Figures
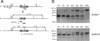

References
-
- Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Edlund H. The morphogenesis of the pancreatic mesenchyme is uncoupled from that of the pancreatic epithelium in IPF1/PDX1-deficient mice. Development. 1996;122:1409–1416. - PubMed
-
- Ahlgren U, Pfaff SL, Jessell TM, Edlund T, Edlund H. Independent requirement for ISL1 in formation of pancreatic mesenchyme and islet cells. Nature. 1997;385:257–260. - PubMed
-
- Apelqvist A, Ahlgren U, Edlund H. Sonic hedgehog directs specialised mesoderm differentiation in the intestine and pancreas. Curr Biol. 1997;7:801–804. - PubMed
-
- Birkedahl-Hansen H. Proteolytic remodeling of extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995;7:728–735. - PubMed
-
- Bradley A. Production and analysis of chimaeric mice. In: Robertson EJ, editor. Teratocarcinomas and embryonic stem cells: A practical approach. Oxford, UK: IRL Press; 1987. pp. 113–151.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
