BMP4 is essential for lens induction in the mouse embryo
- PMID: 9851982
- PMCID: PMC317259
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.23.3764
BMP4 is essential for lens induction in the mouse embryo
Abstract
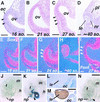
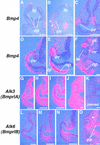
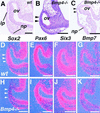
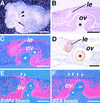
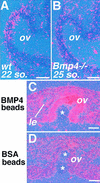
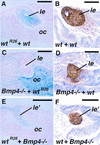
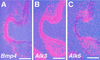
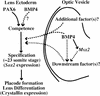
Vertebrate lens development is a classical model system for studying embryonic tissue interactions. Little is known, however, about the molecules mediating such inductive events. Here, we show that Bmp4, which is expressed strongly in the optic vesicle and weakly in the surrounding mesenchyme and surface ectoderm, has crucial roles during lens induction. In Bmp4(tm1) homozygous null mutant embryos, lens induction is absent, but the process can be rescued by exogenous BMP4 protein applied into the optic vesicle in explant cultures. This is associated with rescue of ectodermal expression of Sox2, an early lens placode marker. Substituting the optic vesicle in explant cultures with BMP4-carrying beads, however, does not lead to lens induction, indicating that other factors produced by the optic vesicle are involved. BMP4 appears to regulate expression of a putative downstream gene, Msx2, in the optic vesicle. No change in Pax6 expression is seen in Bmp4(tm1) mutant eyes, and Bmp4 expression appears unaffected in the eyes of homozygous Pax6(Sey-1Neu), suggesting that PAX6 and BMP4 function independently. Based on these results we propose that BMP4 is required for the optic vesicle to manifest its lens-inducing activity, by regulating downstream genes and/or serving as one component of multiple inductive signals.
Figures

References
-
- Chanut F, Heberlein U. Role of decapentaplegic in initiation and progression of the morphogenetic furrow in the developing Drosophila retina. Development. 1997;124:559–567. - PubMed
-
- de Iongh R, Lovicu FJ, Hanneken A, McAvoy JW. Spatio-temporal distribution of acidic and basic FGF indicates a role for FGF in rat lens morphogenesis. Dev Dyn. 1993;198:190–202. - PubMed
-
- Dewulf N, Verschueren K, Lonnoy O, Moren A, Grimsby S, Vande Spiegle K, Miyazono K, Huylebroeck D, Ten Dijke, P P. Distinct spatial and temporal expression patterns of two type I receptors for bone morphogenetic proteins during mouse embryogenesis. Endocrinology. 1995;136:2652–2663. - PubMed
-
- Dudley AT, Lyons KM, Robertson EJ. A requirement for bone morphogenetic protein-7 during development of the mammalian kidney and eye. Genes & Dev. 1995;9:2795–2807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
