Campylobacter fetus surface layer proteins are transported by a type I secretion system
- PMID: 9851986
- PMCID: PMC107744
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.24.6450-6458.1998
Campylobacter fetus surface layer proteins are transported by a type I secretion system
Abstract
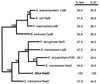
The virulence of Campylobacter fetus, a bacterial pathogen of ungulates and humans, is mediated in part by the presence of a paracrystalline surface layer (S-layer) that confers serum resistance. The subunits of the S-layer are S-layer proteins (SLPs) that are secreted in the absence of an N-terminal signal sequence and attach to either type A or B C. fetus lipopolysaccharide in a serospecific manner. Antigenic variation of multiple SLPs (encoded by sapA homologs) of type A strain 23D occurs by inversion of a promoter-containing DNA element flanked by two sapA homologs. Cloning and sequencing of the entire 6.2-kb invertible region from C. fetus 23D revealed a probable 5.6-kb operon of four overlapping genes (sapCDEF, with sizes of 1,035, 1,752, 1,284, and 1,302 bp, respectively) transcribed in the opposite direction from sapA. The four genes also were present in the invertible region of type B strain 84-107 and were virtually identical to their counterparts in the type A strain. Although SapC had no database homologies, SapD, SapE, and SapF had predicted amino acid homologies with type I protein secretion systems (typified by Escherichia coli HlyBD/TolC or Erwinia chrysanthemi PrtDEF) that utilize C-terminal secretion signals to mediate the secretion of hemolysins, leukotoxins, or proteases from other bacterial species. Analysis of the C termini of four C. fetus SLPs revealed conserved structures that are potential secretion signals. A C. fetus sapD mutant neither produced nor secreted SLPs. E. coli expressing C. fetus sapA and sapCDEF secreted SapA, indicating that the sapCDEF genes are sufficient for SLP secretion. C. fetus SLPs therefore are transported to the cell surface by a type I secretion system.
Figures

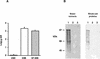


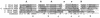
References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. Vol. 1. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1997.
-
- Bachman B J. Derivations and genotypes of some mutant derivatives of Escherichia coli K-12. In: Neidhardt F C, Ingraham J L, Low K B, Magasanik B, Schaechter M, Umbarger H E, editors. Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. Vol. 2. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1987. pp. 1190–1219.
-
- Binet R, Wandersman C. Cloning of the Serratia marcescens hasF gene encoding the Has ABC exporter outer membrane component: a TolC analogue. Mol Microbiol. 1997;22:265–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

