A putative multisubunit Na+/H+ antiporter from Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 9852009
- PMCID: PMC107768
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.24.6642-6648.1998
A putative multisubunit Na+/H+ antiporter from Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
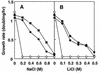
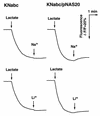
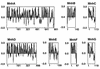
We cloned several genes encoding an Na+/H+ antiporter of Staphylococcus aureus from chromosomal DNA by using an Escherichia coli mutant, lacking all of the major Na+/H+ antiporters, as the host. E. coli cells harboring plasmids for the cloned genes were able to grow in medium containing 0.2 M NaCl (or 10 mM LiCl). Host cells without the plasmids were unable to grow under the same conditions. Na+/H+ antiport activity was detected in membrane vesicles prepared from transformants. We determined the nucleotide sequence of the cloned 7-kbp region. We found that seven open reading frames (ORFs) were necessary for antiporter function. A promoter-like sequence was found in the upstream region from the first ORF. One inverted repeat followed by a T-cluster, which may function as a terminator, was found in the downstream region from the seventh ORF. Neither terminator-like nor promoter-like sequences were found between the ORFs. Thus, it seems that the seven ORFs comprise an operon and that the Na+/H+ antiporter consists of seven kinds of subunits, suggesting that this is a novel type of multisubunit Na+/H+ antiporter. Hydropathy analysis of the deduced amino acid sequences of the seven ORFs suggested that all of the proteins are hydrophobic. As a result of a homology search, we found that components of the respiratory chain showed sequence similarity with putative subunits of the Na+/H+ antiporter. We observed a large Na+ extrusion activity, driven by respiration in E. coli cells harboring the plasmid carrying the genes. The Na+ extrusion was sensitive to an H+ conductor, supporting the idea that the system is not a respiratory Na+ pump but an Na+/H+ antiporter. Introduction of the plasmid into E. coli mutant cells, which were unable to grow under alkaline conditions, enabled the cells to grow under such conditions.
Figures
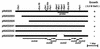

Similar articles
-
A major Li(+) extrusion system NhaB of Pseudomonas aeruginosa : comparison with the major Na(+) extrusion system NhaP.Microbiol Immunol. 2004;48(4):243-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2004.tb03520.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15107534
-
nhaG Na(+)/H(+) antiporter gene of Bacillus subtilis ATCC9372, which is missing in the complete genome sequence of strain 168, and properties of the antiporter.J Biochem. 2001 Nov;130(5):711-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003038. J Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11686935
-
Cloning and sequencing of a novel Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Jul 9;1398(3):330-4. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(98)00058-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9655928
-
The Na+/H+ antiporter of alkaliphilic Bacillus sp.Extremophiles. 2000 Oct;4(5):253-8. doi: 10.1007/s007920070010. Extremophiles. 2000. PMID: 11057908 Review.
-
Na(+)/H(+) antiporters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 May 1;1505(1):144-57. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(00)00284-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11248196 Review.
Cited by
-
Inorganic carbon transporters of the cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism.Photosynth Res. 2011 Sep;109(1-3):47-57. doi: 10.1007/s11120-010-9608-y. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Photosynth Res. 2011. PMID: 21359551 Review.
-
Complete genome sequence of Exiguobacterium profundum TSS-3 isolated from an extremely saline-alkaline spring located in Ixtapa, Chiapas-México.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023 Sep 19;12(9):e0017123. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00171-23. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023. PMID: 37606375 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and identification of Group 1 mrp operon encoding a novel monovalent cation/proton antiporter system from the moderate halophile Halomonas zhaodongensis.Extremophiles. 2014 Nov;18(6):963-72. doi: 10.1007/s00792-014-0666-5. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Extremophiles. 2014. PMID: 24996797
-
Building a genome-based understanding of bacterial pH preferences.Sci Adv. 2023 Apr 28;9(17):eadf8998. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf8998. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37115929 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus MnhF mediates cholate efflux and facilitates survival under human colonic conditions.Infect Immun. 2015 Jun;83(6):2350-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00238-15. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25824834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akamatsu, Y., and T. Tsuchiya. Unpublished results.
-
- Anderson S, de Bruijn M H, Coulson A R, Eperon I C, Sanger F, Young I G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982;156:683–717. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1987. p. 1.1.2.
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1987. p. 2.4.3.
-
- Chen C C, Tsuchiya T, Yamane Y, Wood J M, Wilson T H. Na+(Li+)-proline cotransport in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1985;84:157–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

