The modified beta-ketoadipate pathway in Rhodococcus rhodochrous N75: enzymology of 3-methylmuconolactone metabolism
- PMID: 9852013
- PMCID: PMC107772
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.24.6668-6673.1998
The modified beta-ketoadipate pathway in Rhodococcus rhodochrous N75: enzymology of 3-methylmuconolactone metabolism
Abstract
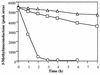
Rhodococcus rhodochrous N75 is able to metabolize 4-methylcatechol via a modified beta-ketoadipate pathway. This organism has been shown to activate 3-methylmuconolactone by the addition of coenzyme A (CoA) prior to hydrolysis of the butenolide ring. A lactone-CoA synthetase is induced by growth of R. rhodochrous N75 on p-toluate as a sole source of carbon. The enzyme has been purified 221-fold by ammonium sulfate fractionation, hydrophobic chromatography, gel filtration, and anion-exchange chromatography. The enzyme, termed 3-methylmuconolactone-CoA synthetase, has a pH optimum of 8.0, a native Mr of 128,000, and a subunit Mr of 62,000, suggesting that the enzyme is homodimeric. The enzyme is very specific for its 3-methylmuconolactone substrate and displays little or no activity with other monoene and diene lactone analogues. Equimolar amounts of these lactone analogues brought about less than 30% (most brought about less than 15%) inhibition of the CoA synthetase reaction with its natural substrate.
Figures

References
-
- Barnett J A, Ingram M. Technique in the study of yeast assimilation reactions. J Appl Bacteriol. 1955;18:131–148.
-
- Blakley E R. The microbial degradation of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid by a β-oxidation pathway with simultaneous induction to the utilisation of benzoate. Can J Microbiol. 1978;24:847–855. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein, utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Bruce N C, Cain R B. β-Methylmuconolactone, a key intermediate in the dissimilation of methylaromatic compounds by a modified 3-oxoadipate pathway evolved in nocardioform actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1988;50:233–239.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

