Selectivity of ferric enterobactin binding and cooperativity of transport in gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 9852016
- PMCID: PMC107775
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.24.6689-6696.1998
Selectivity of ferric enterobactin binding and cooperativity of transport in gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
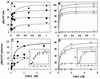
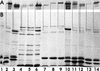
The ligand-gated outer membrane porin FepA serves Escherichia coli as the receptor for the siderophore ferric enterobactin. We characterized the ability of seven analogs of enterobactin to supply iron via FepA by quantitatively measuring the binding and transport of their 59Fe complexes. The experiments refuted the idea that chirality of the iron complex affects its recognition by FepA and demonstrated the necessity of an unsubstituted catecholate coordination center for binding to the outer membrane protein. Among the compounds we tested, only ferric enantioenterobactin, the synthetic, left-handed isomer of natural enterobactin, and ferric TRENCAM, which substitutes a tertiary amine for the macrocyclic lactone ring of ferric enterobactin but maintains an unsubstituted catecholate iron complex, were recognized by FepA (Kd approximately 20 nM). Ferric complexes of other analogs (TRENCAM-3,2-HOPO; TREN-Me-3,2-HOPO; MeMEEtTAM; MeME-Me-3,2-HOPO; K3MECAMS; agrobactin A) with alterations to the chelating groups and different net charge on the iron center neither adsorbed to nor transported through FepA. We also compared the binding and uptake of ferric enterobactin by homologs of FepA from Bordetella bronchisepticus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella typhimurium in the native organisms and as plasmid-mediated clones expressed in E. coli. All the transport proteins bound ferric enterobactin with high affinity (Kd </= 100 nM) and transported it at comparable rates (>/=50 pmol/min/10(9) cells) in their own particular membrane environments. However, the FepA and IroN proteins of S. typhimurium failed to efficiently function in E. coli. For E. coli, S. typhimurium, and P. aeruginosa, the rate of ferric enterobactin uptake was a sigmoidal function of its concentration, indicating a cooperative transport reaction involving multiple interacting binding sites on FepA.
Figures
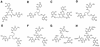

Similar articles
-
Evolution of the ferric enterobactin receptor in gram-negative bacteria.J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):5964-74. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.5964-5974.1991. J Bacteriol. 1991. PMID: 1717434 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of loop deletions on the binding and transport of ferric enterobactin by FepA.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Jun;32(6):1153-65. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01424.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10383757
-
Salmonella typhimurium IroN and FepA proteins mediate uptake of enterobactin but differ in their specificity for other siderophores.J Bacteriol. 1999 Jun;181(11):3610-2. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.11.3610-3612.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10348879 Free PMC article.
-
Three paradoxes of ferric enterobactin uptake.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:s1422-36. doi: 10.2741/1233. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957833 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of ferricsiderophore passage through the outer membrane receptor proteins of Escherichia coli.Biometals. 2007 Jun;20(3-4):263-74. doi: 10.1007/s10534-006-9060-9. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Biometals. 2007. PMID: 17186377 Review.
Cited by
-
The BfeR regulator mediates enterobactin-inducible expression of Bordetella enterobactin utilization genes.J Bacteriol. 2004 Nov;186(21):7302-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7302-7311.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15489442 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the Molecular Structures of Ferric Enterobactin and Ferric Enantioenterobactin Using Racemic Crystallography.J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Oct 25;139(42):15245-15250. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b09375. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 28956921 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the putative siderophore receptor gene bfrZ is controlled by the extracytoplasmic-function sigma factor BupI in Bordetella bronchiseptica.J Bacteriol. 2001 May;183(9):2910-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.9.2910-2917.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11292812 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial iron transport via a siderophore shuttle: a membrane ion transport paradigm.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Sep 26;97(20):10691-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.200318797. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10995480 Free PMC article.
-
Enterobactin-mediated delivery of β-lactam antibiotics enhances antibacterial activity against pathogenic Escherichia coli.J Am Chem Soc. 2014 Jul 9;136(27):9677-91. doi: 10.1021/ja503911p. Epub 2014 Jun 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2014. PMID: 24927110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ames G F-L. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:633–644. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S A, Francis C A, McIntosh M A. Molecular analysis of the Escherichia coli ferric enterobactin in receptor FepA. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:14536–14543. - PubMed
-
- Beall B, Sanden G N. A Bordetella pertussis fepA homologue required for utilization of exogenous ferric enterobactin. Microbiology. 1995;141:3193–3205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

