Selectivity of ferric enterobactin binding and cooperativity of transport in gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 9852016
- PMCID: PMC107775
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.24.6689-6696.1998
Selectivity of ferric enterobactin binding and cooperativity of transport in gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
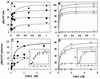
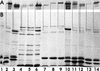
The ligand-gated outer membrane porin FepA serves Escherichia coli as the receptor for the siderophore ferric enterobactin. We characterized the ability of seven analogs of enterobactin to supply iron via FepA by quantitatively measuring the binding and transport of their 59Fe complexes. The experiments refuted the idea that chirality of the iron complex affects its recognition by FepA and demonstrated the necessity of an unsubstituted catecholate coordination center for binding to the outer membrane protein. Among the compounds we tested, only ferric enantioenterobactin, the synthetic, left-handed isomer of natural enterobactin, and ferric TRENCAM, which substitutes a tertiary amine for the macrocyclic lactone ring of ferric enterobactin but maintains an unsubstituted catecholate iron complex, were recognized by FepA (Kd approximately 20 nM). Ferric complexes of other analogs (TRENCAM-3,2-HOPO; TREN-Me-3,2-HOPO; MeMEEtTAM; MeME-Me-3,2-HOPO; K3MECAMS; agrobactin A) with alterations to the chelating groups and different net charge on the iron center neither adsorbed to nor transported through FepA. We also compared the binding and uptake of ferric enterobactin by homologs of FepA from Bordetella bronchisepticus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella typhimurium in the native organisms and as plasmid-mediated clones expressed in E. coli. All the transport proteins bound ferric enterobactin with high affinity (Kd </= 100 nM) and transported it at comparable rates (>/=50 pmol/min/10(9) cells) in their own particular membrane environments. However, the FepA and IroN proteins of S. typhimurium failed to efficiently function in E. coli. For E. coli, S. typhimurium, and P. aeruginosa, the rate of ferric enterobactin uptake was a sigmoidal function of its concentration, indicating a cooperative transport reaction involving multiple interacting binding sites on FepA.
Figures
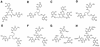

References
-
- Ames G F-L. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:633–644. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S A, Francis C A, McIntosh M A. Molecular analysis of the Escherichia coli ferric enterobactin in receptor FepA. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:14536–14543. - PubMed
-
- Beall B, Sanden G N. A Bordetella pertussis fepA homologue required for utilization of exogenous ferric enterobactin. Microbiology. 1995;141:3193–3205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

