Genome size, complexity, and ploidy of the pathogenic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum
- PMID: 9852017
- PMCID: PMC107776
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.24.6697-6703.1998
Genome size, complexity, and ploidy of the pathogenic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum
Abstract
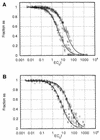
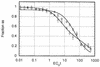
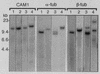
The genome size, complexity, and ploidy of the dimorphic pathogenic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum was determined by using DNA renaturation kinetics, genomic reconstruction, and flow cytometry. Nuclear DNA was isolated from two strains, G186AS and Downs, and analyzed by renaturation kinetics and genomic reconstruction with three putative single-copy genes (calmodulin, alpha-tubulin, and beta-tubulin). G186AS was found to have a genome of approximately 2.3 x 10(7) bp with less than 0.5% repetitive sequences. The Downs strain, however, was found to have a genome approximately 40% larger with more than 16 times more repetitive DNA. The Downs genome was determined to be 3.2 x 10(7) bp with approximately 8% repetitive DNA. To determine ploidy, the DNA mass per cell measured by flow cytometry was compared with the 1n genome estimate to yield a DNA index (DNA per cell/1n genome size). Strain G186AS was found to have a DNA index of 0.96, and Downs had a DNA index of 0.94, indicating that both strains are haploid. Genomic reconstruction and Southern blot data obtained with alpha- and beta-tubulin probes indicated that some genetic duplication has occurred in the Downs strain, which may be aneuploid or partially diploid.
Figures

References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons; 1993.
-
- Berliner M D. Primary subcultures of Histoplasma capsulatum: I. macro- and micromorphology of the mycelial phase. Sabouraudia. 1968;6:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Britten R J, Graham D E, Neufeld B R. Analysis of repeating DNA sequences by reassociation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:363–418. - PubMed
-
- Dressler L G, Seame R L C, Owens M A, Clark G M, McGuire W L. DNA flow cytometry and prognostic factors in 1331 frozen breast cancer specimens. Cancer. 1988;61:420–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

