Calcium and protein kinase C regulate the actin cytoskeleton in the synaptic terminal of retinal bipolar cells
- PMID: 9852158
- PMCID: PMC2132988
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.143.6.1661
Calcium and protein kinase C regulate the actin cytoskeleton in the synaptic terminal of retinal bipolar cells
Abstract
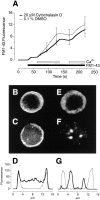
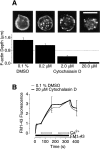
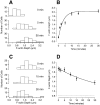
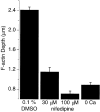
The organization of filamentous actin (F-actin) in the synaptic pedicle of depolarizing bipolar cells from the goldfish retina was studied using fluorescently labeled phalloidin. The amount of F-actin in the synaptic pedicle relative to the cell body increased from a ratio of 1.6 +/- 0.1 in the dark to 2.1 +/- 0.1 after exposure to light. Light also caused the retraction of spinules and processes elaborated by the synaptic pedicle in the dark. Isolated bipolar cells were used to characterize the factors affecting the actin cytoskeleton. When the electrical effect of light was mimicked by depolarization in 50 mM K+, the actin network in the synaptic pedicle extended up to 2.5 micrometer from the plasma membrane. Formation of F-actin occurred on the time scale of minutes and required Ca2+ influx through L-type Ca2+ channels. Phorbol esters that activate protein kinase C (PKC) accelerated growth of F-actin. Agents that inhibit PKC hindered F-actin growth in response to Ca2+ influx and accelerated F-actin breakdown on removal of Ca2+. To test whether activity-dependent changes in the organization of F-actin might regulate exocytosis or endocytosis, vesicles were labeled with the fluorescent membrane marker FM1-43. Disruption of F-actin with cytochalasin D did not affect the continuous cycle of exocytosis and endocytosis that was stimulated by maintained depolarization, nor the spatial distribution of recycled vesicles within the synaptic terminal. We suggest that the actions of Ca2+ and PKC on the organization of F-actin regulate the morphology of the synaptic pedicle under varying light conditions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The kinetics of exocytosis and endocytosis in the synaptic terminal of goldfish retinal bipolar cells.J Physiol. 1999 Feb 15;515 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):181-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.181ad.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9925888 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous vesicle cycling in the synaptic terminal of retinal bipolar cells.Neuron. 1996 Nov;17(5):957-67. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80226-3. Neuron. 1996. PMID: 8938127
-
The actions of barium and strontium on exocytosis and endocytosis in the synaptic terminal of goldfish bipolar cells.J Physiol. 2001 Sep 15;535(Pt 3):809-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-1-00809.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11559777 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes in chromaffin cell cytoskeleton as prelude to exocytosis.Mol Neurobiol. 1992 Winter;6(4):339-58. doi: 10.1007/BF02757940. Mol Neurobiol. 1992. PMID: 1337454 Review.
-
Synaptic release at mammalian bipolar cell terminals.Vis Neurosci. 2011 Jan;28(1):109-19. doi: 10.1017/S0952523810000453. Vis Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21272392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trophoblast glycoprotein is required for efficient synaptic vesicle exocytosis from retinal rod bipolar cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 30;17:1306006. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1306006. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38099150 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic architecture of photoreceptor ribbon synapses: cytoskeletal, extracellular matrix, and intramembrane proteins.Vis Neurosci. 2011 Nov;28(6):453-71. doi: 10.1017/S0952523811000356. Vis Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22192503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocytosis at the synaptic terminal.J Physiol. 2003 Dec 1;553(Pt 2):345-55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049221. Epub 2003 Sep 8. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12963793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tracking quantum dot-tagged calcium channels at vertebrate photoreceptor synapses: retinal slices and dissociated cells.Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2013 Jan;Chapter 2:Unit 2.18. doi: 10.1002/0471142301.ns0218s62. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23315944 Free PMC article.
-
Structural domains involved in the regulation of transmitter release by synapsins.J Neurosci. 2005 Mar 9;25(10):2658-69. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4278-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15758176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey CH, Thompson EB. Indented synapses in Aplysia. . Brain Res. 1979;173:13–20. - PubMed
-
- Behrens UD, Wagner HJ. Adaptation-dependent changes of bipolar cell terminals in fish retina: effects on overall morphology and spinule formation in Ma and Mb cells. Vision Res. 1996;36:3901–3911. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BW, Bamburg JR. Cycling of actin assembly in synaptosomes and neurotransmitter release. Neuron. 1989;3:257–265. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BW, Dewit M, Bamburg JR. Actin disassembles reversibly during electrically induced recycling of synaptic vesicles in cultured neurons. Mol Brain Res. 1998;53:236–250. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

