Release of cAMP gating by the alpha6beta4 integrin stimulates lamellae formation and the chemotactic migration of invasive carcinoma cells
- PMID: 9852165
- PMCID: PMC2132981
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.143.6.1749
Release of cAMP gating by the alpha6beta4 integrin stimulates lamellae formation and the chemotactic migration of invasive carcinoma cells
Abstract
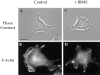
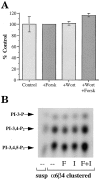
The alpha6beta4 integrin promotes carcinoma in-vasion by its activation of a phosphoinositide 3-OH (PI3-K) signaling pathway (Shaw, L.M., I. Rabinovitz, H.H.-F. Wang, A. Toker, and A.M. Mercurio. Cell. 91: 949-960). We demonstrate here using MDA-MB-435 breast carcinoma cells that alpha6beta4 stimulates chemotactic migration, a key component of invasion, but that it has no influence on haptotaxis. Stimulation of chemotaxis by alpha6beta4 expression was observed in response to either lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) or fibroblast conditioned medium. Moreover, the LPA-dependent formation of lamellae in these cells is dependent upon alpha6beta4 expression. Both lamellae formation and chemotactic migration are inhibited or "gated" by cAMP and our results reveal that a critical function of alpha6beta4 is to suppress the intracellular cAMP concentration by increasing the activity of a rolipram-sensitive, cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE). This PDE activity is essential for lamellae formation, chemotactic migration and invasion based on data obtained with PDE inhibitors. Although PI3-K and cAMP-specific PDE activities are both required to promote lamellae formation and chemotactic migration, our data indicate that they are components of distinct signaling pathways. The essence of our findings is that alpha6beta4 stimulates the chemotactic migration of carcinoma cells through its ability to influence key signaling events that underlie this critical component of carcinoma invasion.
Figures


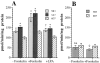


Similar articles
-
Activation of p53 function in carcinoma cells by the alpha6beta4 integrin.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jul 16;274(29):20733-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.29.20733. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10400708
-
Protein kinase C-dependent mobilization of the alpha6beta4 integrin from hemidesmosomes and its association with actin-rich cell protrusions drive the chemotactic migration of carcinoma cells.J Cell Biol. 1999 Sep 6;146(5):1147-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.5.1147. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10477766 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase by the alpha6beta4 integrin promotes carcinoma invasion.Cell. 1997 Dec 26;91(7):949-60. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80486-9. Cell. 1997. PMID: 9428518
-
Towards a mechanistic understanding of tumor invasion--lessons from the alpha6beta 4 integrin.Semin Cancer Biol. 2001 Apr;11(2):129-41. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2000.0364. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001. PMID: 11322832 Review.
-
The alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and epithelial cell migration.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;13(5):541-5. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00249-0. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11544021 Review.
Cited by
-
Traction forces mediated by alpha6beta4 integrin: implications for basement membrane organization and tumor invasion.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Dec;12(12):4030-43. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.12.4030. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11739798 Free PMC article.
-
Use of RNA interference to inhibit integrin (alpha6beta4)-mediated invasion and migration of breast carcinoma cells.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20(6):569-76. doi: 10.1023/a:1025819521707. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003. PMID: 14598892
-
Integrin alpha6beta4 controls the expression of genes associated with cell motility, invasion, and metastasis, including S100A4/metastasin.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 16;284(3):1484-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803997200. Epub 2008 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19011242 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase A governs a RhoA-RhoGDI protrusion-retraction pacemaker in migrating cells.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Jun;13(6):660-7. doi: 10.1038/ncb2231. Epub 2011 May 15. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21572420 Free PMC article.
-
Butyrate inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion.J Gastrointest Surg. 2003 Nov;7(7):864-70. doi: 10.1007/s11605-003-0031-y. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003. PMID: 14592659
References
-
- Aznavoorian S, Stracke ML, Parsons J, McClanahan J, Liotta LA. Integrin αvβ3 mediates chemotactic and haptotactic motility in human melanoma cells through different signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:3247–3254. - PubMed
-
- Borradori L, Sonnenberg A. Hemidesmosomes—roles in adhesion, signaling and human disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:647–656. - PubMed
-
- Chao C, Lotz MM, Clarke AC, Mercurio AM. A function for the integrin α6β4 in the invasive properties of colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4811–4819. - PubMed
-
- Clark EA, Brugge JS. Integrins and signal transduction pathways: The road taken. Science. 1995;268:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Clarke AS, Lotz MM, Chao C, Mercurio AM. Activation of the p21 pathway of growth arrest and apoptosis by the β4integrin cytoplasmic domain. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:22672–22676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

