Cell-type specific expression of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the rat hippocampus
- PMID: 9852317
- PMCID: PMC2269073
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.315ae.x
Cell-type specific expression of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
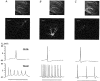
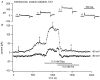
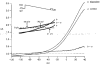
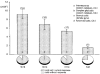
1. The distribution of ATP-sensitive K+ channels (KATP channels) was investigated in four cell types in hippocampal slices prepared from 10- to 13-day-old rats: CA1 pyramidal cells, interneurones of stratum radiatum in CA1, complex glial cells of the same area and granule cells of the dentate gyrus. The neuronal cell types were identified visually and characterized by the shapes and patterns of their action potentials and by neurobiotin labelling. 2. The patch-clamp technique was used to study the sensitivity of whole-cell currents to diazoxide (0.3 mM), a KATP channel opener, and to tolbutamide (0.5 mM) or glibenclamide (20 microM), two KATP channel inhibitors. The fraction of cells in which whole-cell currents were activated by diazoxide and inhibited by tolbutamide was 26% of pyramidal cells, 89 % of interneurones, 100% of glial cells and 89% of granule cells. The reversal potential of the diazoxide-induced current was at the K+ equilibrium potential and a similar current activated spontaneously when cells were dialysed with an ATP-free pipette solution. 3. Using the single-cell RT-PCR method, the presence of mRNA encoding KATP channel subunits (Kir6.1, Kir6.2, SUR1 and SUR2) was examined in CA1 pyramidal cells and interneurones. Subunit mRNA combinations that can result in functional KATP channels (Kir6.1 together with SUR1, Kir6.2 together with SUR1 or SUR2) were detected in only 17% of the pyramidal cells. On the other hand, KATP channels may be formed in 75% of the interneurones, mainly by the combination of Kir6.2 with SUR1 (58% of all interneurones). 4. The results of these combined analyses indicate that functional KATP channels are present in principal neurones, interneurones and glial cells of the rat hippocampus, but at highly different densities in the four cell types studied.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels during energy depletion in CA1 pyramidal cells and interneurones of rat hippocampus.Pflugers Arch. 2000 Jan;439(3):256-62. doi: 10.1007/s004249900184. Pflugers Arch. 2000. PMID: 10650976
-
Cell-type specific depression of neuronal excitability in rat hippocampus by activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels.Eur Biophys J. 2002 Oct;31(6):467-77. doi: 10.1007/s00249-002-0241-3. Epub 2002 Aug 9. Eur Biophys J. 2002. PMID: 12355256
-
Functional coupling between sulfonylurea receptor type 1 and a nonselective cation channel in reactive astrocytes from adult rat brain.J Neurosci. 2003 Sep 17;23(24):8568-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-24-08568.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 13679426 Free PMC article.
-
A view of sur/KIR6.X, KATP channels.Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:667-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.60.1.667. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9558481 Review.
-
ATP-sensitive potassium channels: a model of heteromultimeric potassium channel/receptor assemblies.Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:337-62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.61.1.337. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10099692 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular correlates of the M-current in cultured rat hippocampal neurons.J Physiol. 2002 Oct 1;544(Pt 1):29-37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.028571. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12356878 Free PMC article.
-
Mice transgenically overexpressing sulfonylurea receptor 1 in forebrain resist seizure induction and excitotoxic neuron death.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Mar 13;98(6):3549-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.051012898. Epub 2001 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11248115 Free PMC article.
-
CA1 pyramidal cells have diverse biophysical properties, affected by development, experience, and aging.PeerJ. 2017 Sep 19;5:e3836. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3836. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28948109 Free PMC article.
-
Caloric Restriction and Ketogenic Diet Therapy for Epilepsy: A Molecular Approach Involving Wnt Pathway and KATP Channels.Front Neurol. 2020 Nov 5;11:584298. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.584298. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33250850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAD-dependent regulation of fuel metabolism and K(ATP) channel activity confers resistance to epileptic seizures.Neuron. 2012 May 24;74(4):719-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.032. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22632729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer C, ten Bruggencate G. Actions of BRL 34915 (cromakalim) upon convulsive discharges in guinea pig hippocampal slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 1988;337:429–434. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft SJH, Ashcroft FM. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cellular Signalling. 1990;2:197–214. 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-F. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashford MLJ, Boden PR, Treherne JM. Glucose-induced excitation of hypothalamic neurones is mediated by ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Pflügers Archiv. 1990;415:479–483. - PubMed
-
- Audinat E, Lambolez B, Rossier J, Crépel F. Activity-dependent regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit expression in rat cerebellar granule cells. European Journal of Neuroscience. 1994;6:1792–1800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

