Development of a Plasmodium PCR for monitoring efficacy of antimalarial treatment
- PMID: 9854060
- PMCID: PMC84160
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.1.35-38.1999
Development of a Plasmodium PCR for monitoring efficacy of antimalarial treatment
Abstract
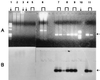
We report in this work a highly sensitive and nonradioactive PCR method for the detection of the four species of parasite causing human malaria. Plasmodium-specific primers corresponding to the small-subunit rRNA genes of the malaria parasite were used, and a 291-bp fragment was amplified. Our results showed a high specificity for the four human Plasmodium species, and we were able to detect one parasite in 50 microl of whole blood. The responses of 12 patients infected with Plasmodium falciparum to antimalarial therapy were monitored by PCR diagnosis and examination of thick blood film for at least 20 min by an experienced microscopist. For one patient this study allowed early diagnosis of therapeutic failure, confirmed 7 days later by examination of the thick blood film. A total of 134 samples were examined; 94 were positive by PCR, and among these 68 were positive by thick blood film examination. The sensitivity of the thick blood film was 72.3% compared to PCR and 60.7% compared to dot blot hybridization.
Figures

References
-
- Abdullah N R, Furuta T, Taib R, Kita K, Kojima S, Wah M J. Short report: development of a new diagnostic method for Plasmodium falciparum infection using a reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1996;54:162–163. - PubMed
-
- Arai M, Mizukoshi C, Kubochi F, Kakutani T, Wataya Y. Detection of Plasmodium falciparum in human blood by a nested polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;51:617–626. - PubMed
-
- Barker R J, Banchongaksorn T, Courval J M, Suwonkerd W, Rimwungtragoon K, Wirth D F. A simple method to detect Plasmodium falciparum directly from blood samples using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992;46:416–426. - PubMed
-
- Beadle C, Long G W, Weiss W R, McElroy P D, Maret S M, Oloo A J, Hoffman S L. Diagnosis of malaria by detection of Plasmodium falciparum HRP-2 antigen with a rapid dipstick antigen-capture assay. Lancet. 1994;343:564–568. - PubMed
-
- Bottius E, Guanzirolli A, Trape J, Rogier C, Konate L, Druilhe P. Malaria: even more chronic in nature than previously thought; evidence for subpatient parasitaemia detectable by the polymerase chain reaction. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1996;90:15–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

