Nucleic acid-based cross-linking assay for detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA
- PMID: 9854083
- PMCID: PMC84196
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.1.161-164.1999
Nucleic acid-based cross-linking assay for detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA
Abstract
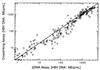
A nucleic acid photo-cross-linking technology was used to develop a direct assay for the quantification of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA levels in serum. Cross-linker-modified DNA probes complementary to the viral genomes of the major HBV subtypes were synthesized and used in an assay that could be completed in less than 6 h. The quantification range of the assay, as determined by testing serial dilutions of Eurohep HBV reference standards and cloned HBV DNA, was 5 x 10(5) to 3 x 10(9) molecules of HBV DNA/ml of serum. Within-run and between-run coefficients of variation (CVs) for the assay were 4. 3 and 4.0%, respectively. The assay was used to determine HBV DNA levels in 302 serum samples, and the results were compared to those obtained after testing the same samples with the Chiron branched-DNA (bDNA) assay for HBV DNA. Of the samples tested, 218 were positive for HBV DNA by both assays and 72 gave results below the cutoff for both assays. Of the remaining 12 samples, 10 were positive for HBV DNA by the cross-linking assay only; the 2 other samples were positive by the bDNA assay only. Twenty-eight samples had to be retested by the bDNA assay (CV, >20% between the results obtained from the testing of each sample in duplicate), whereas only three samples required retesting by the cross-linking assay. The correlation between the HBV DNA levels, as measured by the two tests, was very high (r = 0.902; P = 0.01). We conclude that the cross-linking assay is a sensitive and reproducible method for the detection and quantification of HBV DNA levels in serum.
Figures

References
-
- Aach R A. The treatment of chronic type B viral hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1988;109:89–90. - PubMed
-
- Alter M J, Mast E E. The epidemiology of viral hepatitis in the United States. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 1994;23:437–455. - PubMed
-
- Butterworth L A, Prior S L, Buda P J, Faoagali J L, Cooksley W G E. Comparison of four methods for quantitative measurement of hepatitis B viral DNA. J Hepatol. 1996;24:686–691. - PubMed
-
- Carman W F, Jacyna M R, Hadziyannis S, Karayiannis P, McGarvey M J, Makris A, Thomas H C. Mutation preventing formation of e antigen in patients with chronic HBV infection. Lancet. 1989;ii:588–591. - PubMed
-
- Gerlich W H, Heermann K H, Thomssen R the Eurohep Group. Quantitative assays for hepatitis B virus DNA: standardization and quality control. Viral Hepatitis Rev. 1995;1:53–57.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

