Viral immune evasion due to persistence of activated T cells without effector function
- PMID: 9858507
- PMCID: PMC2212420
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.12.2205
Viral immune evasion due to persistence of activated T cells without effector function
Abstract
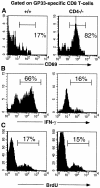
We examined the regulation of virus-specific CD8 T cell responses during chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection of mice. Our study shows that within the same persistently infected host, different mechanisms can operate to silence antiviral T cell responses; CD8 T cells specific to one dominant viral epitope were deleted, whereas CD8 T cells responding to another dominant epitope persisted indefinitely. These virus-specific CD8 T cells expressed activation markers (CD69(hi), CD44(hi), CD62Llo) and proliferated in vivo but were unable to elaborate any antiviral effector functions. This unresponsive phenotype was more pronounced under conditions of CD4 T cell deficiency, highlighting the importance of CD8- CD4 T cell collaboration in controlling persistent infections. Importantly, in the presence of CD4 T cell help, adequate CD8 effector activity was maintained and the chronic viral infection eventually resolved. The persistence of activated virus-specific CD8 T cells without effector function reveals a novel mechanism for silencing antiviral immune responses and also offers new possibilities for enhancing CD8 T cell immunity in chronically infected hosts.
Figures
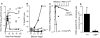


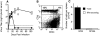
Comment in
-
The critical need for CD4 help in maintaining effective cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses.J Exp Med. 1998 Dec 21;188(12):2199-204. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.12.2199. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9858506 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kägi D, Ledermann B, Burki K, Seiler P, Odermatt B, Olsen KJ, Podack ER, Zinkernagel RM, Hengartner H. Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature. 1994;369:31–37. - PubMed
-
- Tishon A, Lewicki H, Rall G, Von Herrath M, Oldstone MBA. An essential role for type 1 interferon-γ in terminating persistent viral infection. Virology. 1995;212:244–250. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed R, Gray D. Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science. 1996;272:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Doherty PC. Cytotoxic T cell effector and memory function in viral immunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;206:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

