CA- and purine-rich elements form a novel bipartite exon enhancer which governs inclusion of the minute virus of mice NS2-specific exon in both singly and doubly spliced mRNAs
- PMID: 9858560
- PMCID: PMC83894
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.1.364
CA- and purine-rich elements form a novel bipartite exon enhancer which governs inclusion of the minute virus of mice NS2-specific exon in both singly and doubly spliced mRNAs
Abstract
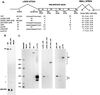
The alternatively spliced 290-nucleotide NS2-specific exon of the parvovirus minute virus of mice (MVM), which is flanked by a large intron upstream and a small intron downstream, constitutively appears both in the R1 mRNA as part of a large 5'-terminal exon (where it is translated in open reading frame 3 [ORF3]), and in the R2 mRNA as an internal exon (where it is translated in ORF2). We have identified a novel bipartite exon enhancer element, composed of CA-rich and purine-rich elements within the 5' and 3' regions of the exon, respectively, that is required to include NS2-specific exon sequences in mature spliced mRNA in vivo. These two compositionally different enhancer elements are somewhat redundant in function: either element alone can at least partially support exon inclusion. They are also interchangeable: either element can function at either position. Either a strong 3' splice site upstream (i.e., the exon 5' terminus) or a strong 5' splice site downstream (i.e., the exon 3' terminus) is sufficient to prevent skipping of the NS2-specific exon, and a functional upstream 3' splice site is required for inclusion of the NS2-specific exon as an internal exon into the mature, doubly spliced R2 mRNA. The bipartite enhancer functionally strengthens these termini: the requirement for both the CA-rich and purine-rich elements can be overcome by improvements to the polypyrimidine tract of the upstream intron 3' splice site, and the purine-rich element also supports exon inclusion mediated through the downstream 5' splice sites. In summary, a suboptimal large-intron polypyrimidine tract, sequences within the downstream small intron, and a novel bipartite exonic enhancer operate together to yield the balanced levels of R1 and R2 observed in vivo. We suggest that the unusual bipartite exonic enhancer functions to mediate proper levels of inclusion of the NS2-specific exon in both singly spliced R1 and doubly spliced R2.
Figures







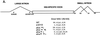
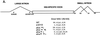
Similar articles
-
Inclusion of the NS2-specific exon in minute virus of mice mRNA is facilitated by an intronic splicing enhancer that affects definition of the downstream small intron.Virology. 1999 May 25;258(1):84-94. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9696. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10329570
-
A premature termination codon interferes with the nuclear function of an exon splicing enhancer in an open reading frame-dependent manner.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):1640-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1640. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10022852 Free PMC article.
-
Sequences within the parvovirus minute virus of mice NS2-specific exon are required for inclusion of this exon into spliced steady-state RNA.J Virol. 1995 Sep;69(9):5864-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.9.5864-5868.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7637034 Free PMC article.
-
Exonization of transposed elements: A challenge and opportunity for evolution.Biochimie. 2011 Nov;93(11):1928-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.014. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21787833 Review.
-
Regulation of alternative RNA splicing by exon definition and exon sequences in viral and mammalian gene expression.J Biomed Sci. 2004 May-Jun;11(3):278-94. doi: 10.1007/BF02254432. J Biomed Sci. 2004. PMID: 15067211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selectable system for monitoring the instability of CTG/CAG triplet repeats in mammalian cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jul;23(13):4485-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.13.4485-4493.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12808091 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing of the large intron present in the nonstructural gene of minute virus of mice is governed by TIA-1/TIAR binding downstream of the nonconsensus donor.J Virol. 2009 Jun;83(12):6306-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00213-09. Epub 2009 Apr 1. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19339348 Free PMC article.
-
A splicing enhancer in the E4 coding region of human papillomavirus type 16 is required for early mRNA splicing and polyadenylation as well as inhibition of premature late gene expression.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(18):12002-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.12002-12015.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16140776 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 late-stage-specific nucleotide 3605 3' splice site is modulated by a novel exonic bipartite regulator but not by an intronic purine-rich element.J Virol. 2000 Nov;74(22):10612-22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10612-10622.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11044105 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA binding protein YB-1 binds A/C-rich exon enhancers and stimulates splicing of the CD44 alternative exon v4.EMBO J. 2001 Jul 16;20(14):3821-30. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.14.3821. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11447123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berget S M. Exon recognition in vertebrate splicing. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:2411–2444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
