Withdrawal of survival factors results in activation of the JNK pathway in neuronal cells leading to Fas ligand induction and cell death
- PMID: 9858598
- PMCID: PMC83932
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.1.751
Withdrawal of survival factors results in activation of the JNK pathway in neuronal cells leading to Fas ligand induction and cell death
Abstract
The JNK pathway modulates AP-1 activity. While in some cells it may have proliferative and protective roles, in neuronal cells it is involved in apoptosis in response to stress or withdrawal of survival signals. To understand how JNK activation leads to apoptosis, we used PC12 cells and primary neuronal cultures. In PC12 cells, deliberate JNK activation is followed by induction of Fas ligand (FasL) expression and apoptosis. JNK activation detected by c-Jun phosphorylation and FasL induction are also observed after removal of either nerve growth factor from differentiated PC12 cells or KCl from primary cerebellar granule neurons (CGCs). Sequestation of FasL by incubation with a Fas-Fc decoy inhibits apoptosis in all three cases. CGCs derived from gld mice (defective in FasL) are less sensitive to apoptosis caused by KCl removal than wild-type neurons. In PC12 cells, protection is also conferred by a c-Jun mutant lacking JNK phosphoacceptor sites and a small molecule inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and JNK, which inhibits FasL induction. Hence, the JNK-to-c-Jun-to-FasL pathway is an important mediator of stress-induced neuronal apoptosis.
Figures
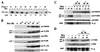
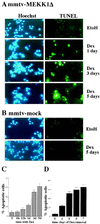
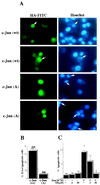

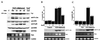
Similar articles
-
Sustained activation of JNK/p38 MAPK pathways in response to cisplatin leads to Fas ligand induction and cell death in ovarian carcinoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 23;278(21):19245-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208134200. Epub 2003 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12637505
-
Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis.Science. 1995 Nov 24;270(5240):1326-31. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1326. Science. 1995. PMID: 7481820
-
Role of the Jun kinase pathway in the regulation of c-Jun expression and apoptosis in sympathetic neurons.J Neurosci. 1998 Mar 1;18(5):1713-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-05-01713.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9464996 Free PMC article.
-
The c-Jun N-terminal kinase cascade plays a role in stress-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells by up-regulating Fas ligand expression.J Immunol. 1998 Jan 1;160(1):134-44. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9551965
-
c-Jun and the transcriptional control of neuronal apoptosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1015-21. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00372-5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007936 Review.
Cited by
-
Heroin activates ATF3 and CytC via c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways to mediate neuronal apoptosis.Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2015 Apr 7;21:53-62. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.893827. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2015. PMID: 25848832 Free PMC article.
-
Role of PI 3-kinase, Akt and Bcl-2-related proteins in sustaining the survival of neurotrophic factor-independent adult sympathetic neurons.J Cell Biol. 2001 Sep 3;154(5):995-1005. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200101068. Epub 2001 Aug 27. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11524433 Free PMC article.
-
A novel AP-1 element in the CD95 ligand promoter is required for induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells upon treatment with anticancer drugs.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;20(20):7826-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.20.7826-7837.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11003676 Free PMC article.
-
p38 MAP kinase mediates bax translocation in nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in neurons.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jul 24;150(2):335-47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.2.335. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10908576 Free PMC article.
-
Iron chelator-induced apoptosis via the ER stress pathway in gastric cancer cells.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):9709-19. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4878-4. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26803514
References
-
- Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988;55:875–885. - PubMed
-
- Angel P, Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1072:129–157. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1985;14:375–403. - PubMed
-
- Binétruy B, Smeal T, Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991;351:122–127. - PubMed
-
- Bonfoco E, Leist M, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton S A, Nicotera P. Cytoskeletal breakdown and apoptosis elicited by NO donors in cerebellar granule cells require NMDA receptor activation. J Neurochem. 1996;67:2484–2493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
