Lamellar lipoproteins uniquely contribute to hyperlipidemia in mice doubly deficient in apolipoprotein E and hepatic lipase
- PMID: 9861024
- PMCID: PMC28098
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15647
Lamellar lipoproteins uniquely contribute to hyperlipidemia in mice doubly deficient in apolipoprotein E and hepatic lipase
Abstract
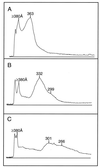
Remnants of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein (apo) B-48 accumulate in apo E-deficient mice, causing pronounced hypercholesterolemia. Mice doubly deficient in apo E and hepatic lipase have more pronounced hypercholesterolemia, even though remnants do not accumulate appreciably in mice deficient in hepatic lipase alone. Here we show that the doubly deficient mice manifest a unique lamellar hyperlipoproteinemia, characterized by vesicular particles 600 A-1,300 A in diameter. As seen by negative-staining electron microscopy, these lipoproteins also contain an electron-lucent region adjacent to the vesicle wall, similar to the core of typical lipoproteins. Correlative chemical analysis indicates that the vesicle wall is composed of a 1:1 molar mixture of cholesterol and phospholipids, whereas the electron-lucent region appears to be composed of cholesteryl esters (about 12% of the particle mass). Like the spherical lipoproteins of doubly deficient mice, the vesicular particles contain apo B-48, but they are particularly rich in apo A-IV. We propose that cholesteryl esters are removed from spherical lipoproteins of these mice by scavenger receptor B1, leaving behind polar lipid-rich particles that fuse to form vesicular lipoproteins. Hepatic lipase may prevent such vesicular lipoproteins from accumulating in apo E-deficient mice by hydrolyzing phosphatidyl choline as scavenger receptor B1 removes the cholesteryl esters and by gradual endocytosis of lipoproteins bound to hepatic lipase on the surface of hepatocytes.
Figures



References
-
- Havel R J. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1995;6:312–316. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S H, Reddick R L, Piedrahita J A, Maeda N. Science. 1992;258:468–471. - PubMed
-
- Plump A, Smith J, Hayek T, Aalto-Setala K, Walsh A, Verstuyft J, Rubin E, Breslow J. Cell. 1992;71:343–353. - PubMed
-
- Ghiselli G, Schaefer E J, Gascon P, Brewer H B., Jr Science. 1981;214:1239–1241. - PubMed
-
- Qiu S, Bergeron N, Kotite L, Krauss R M, Bensadoun A, Havel R J. J Lipid Res. 1998;39:1661–1668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

