Information about movement direction obtained from synchronous activity of motor cortical neurons
- PMID: 9861034
- PMCID: PMC28108
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15706
Information about movement direction obtained from synchronous activity of motor cortical neurons
Abstract
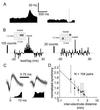
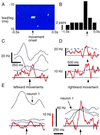
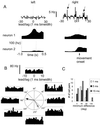
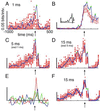
Although neuronal synchronization has been shown to exist in primary motor cortex (MI), very little is known about its possible contribution to coding of movement. By using cross-correlation techniques from multi-neuron recordings in MI, we observed that activity of neurons commonly synchronized around the time of movement initiation. For some cell pairs, synchrony varied with direction in a manner not readily predicted by the firing of either neuron. Information theoretic analysis demonstrated quantitatively that synchrony provides information about movement direction beyond that expected by simple rate changes. Thus, MI neurons are not simply independent encoders of movement parameters but rather engage in mutual interactions that could potentially provide an additional coding dimension in cortex.
Figures
Comment in
-
Information coding in the cortex by independent or coordinated populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Dec 22;95(26):15166-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15166. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9860939 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fu Q-G, Flament D, Coltz J D, Ebner T J. J Neurophysiol. 1995;73:836–854. - PubMed
-
- Fu Q-G, Suarez J I, Ebner T J. J Neurophysiol. 1993;70:2097–2116. - PubMed
-
- Thach W T. J Neurophysiol. 1978;41:654–676. - PubMed
-
- Evarts E V. In: Handbook of Physiology. Brooks V B, editor. Vol. 2. Washington, DC: Am. Physiol. Soc.; 1981. pp. 1083–1120.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

