Frusemide inhibits angiotensin II-induced contraction on human vascular smooth muscle
- PMID: 9862246
- PMCID: PMC1873800
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00820.x
Frusemide inhibits angiotensin II-induced contraction on human vascular smooth muscle
Abstract
Aims: Frusemide is widely used in the treatment of acute pulmonary oedema, chronic congestive heart failure and, to a lesser degree, in the treatment of hypertension. Evidence suggests that frusenuide exerts an anti-vasoconstrictor effect independent of its diuretic properties. Since angiotensin II is a highly potent vasoconstrictor involved in the pathophysiology of these diseases, we have investigated the effect of frusemide on the contraction elicited by angiotensin II on human internal mammary artery (IMA) and saphenous vein (SV).
Methods: Rings of IMA and SV were suspended for isometric tension recording in organ baths. Concentration-response curves to angiotensin II were performed in the absence (control) or in the presence of frusemide (10(-6) to 10(-3) M). In addition, the effect of frusemide was evaluated after cyclooxygenase inhibition by indomethacin (10(-6) M) and was compared with those of the other loop diuretic bumetanide (10(-4) M).
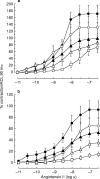
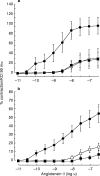
Results: Frusemide induced a concentration-dependent decrease of the contraction elicited by angiotensin II on IMA and SV. On both vessels, the inhibitory effect on the maximal contraction to angiotensin II was significant with concentrations of frusemide from 10(-5) to 10(-3) M. Angiotensin II potency (pD2) was only reduced by 10(-3) M frusemide. The effect of frusemide was not altered in the presence of indomethacin. Bumetanide was less potent than frusemide in inhibiting angiotensin II-induced contractions in both IMA and SV.
Conclusions: Frusemide, at concentrations in the therapeutic range (10(-5) M), inhibits angiotensin II-induced contraction on human isolated IMA and SV. This inhibitory effect is cyclooxygenase independent and appears mediated, at least in part, by inhibition of Na+/K+/2Cl- symport. Reduction in the vasoconstrictor effect of angiotensin 1 may be involved in the therapeutic efficacy of frusemide.
Figures
References
-
- Jackson EK. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9. McGraw-Hill; 1995. Diuretics. In Goodman & Gilman’s; pp. 685–715.
-
- Gerkens JF. Does furosemide have vasodilator activity? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1987;8:254–257.
-
- Ferrario CM. The renin-angiotensin system: importance in physiology and pathology. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15(Supp. 3):S1–S. - PubMed
-
- Johnston GD, Nicholls DP, Leahey WJ, Finch MB. The effects of captopril on the vascular responses to frusemide in man. Clin Sci. 1983;65:359–363. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

