Comparison of the vasoconstrictor effects of rizatriptan and sumatriptan in human isolated cranial arteries: immunohistological demonstration of the involvement of 5-HT1B-receptors
- PMID: 9862247
- PMCID: PMC1873795
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00821.x
Comparison of the vasoconstrictor effects of rizatriptan and sumatriptan in human isolated cranial arteries: immunohistological demonstration of the involvement of 5-HT1B-receptors
Abstract
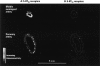
Aims: We compared the vasoconstrictor effects of 5-HT with those of the selective 5-HT1B/1D-receptor agonists sumatriptan and rizatriptan in human isolated cranial (middle meningeal) arteries. In addition selective 5-HT1B- or 5-HT1D-receptor antibodies were used in combination with semiquantitative immunohistochemical techniques to compare the levels of expression of these receptors in human middle meningeal and coronary arteries.
Methods: Middle meningeal and coronary arteries were obtained (with consent) from either neurosurgical patients or donor hearts, respectively. Segments of middle meningeal artery were mounted in organ baths for isometric recording and cumulative concentration-effect curves to 5-HT, rizatriptan and sumatriptan were obtained. Frozen fresh sections of middle meningeal and coronary arteries were subjected to standard immunohistochemical techniques using specific 5-HT1B- or 5-HT1D-receptor primary antibodies and a radiolabelled secondary antibody. Data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and nonlinear regression analysis.
Results: 5-HT, rizatriptan and sumatriptan were potent vasoconstrictors in human isolated middle meningeal artery (EC50 values=32, 90 and 71 nM, respectively). A significantly higher level of 5-HT1B-receptor immunoreactivity was detected in middle meningeal artery compared with coronary artery (ANOVA, F=7.95, DF=1,4, P<0.05).
Conclusions: Rizatriptan and sumatriptan act selectively to cause vasoconstriction in human isolated middle meningeal artery and are 10-fold more potent than in human coronary artery. The higher level of expression of 5-HT1B-receptors in middle meningeal compared with coronary artery provides a pharmacological basis for the craniovascular selectively of both rizatriptan and sumatriptan.
Figures


Similar articles
-
5-HT1B-receptors and vascular reactivity in human isolated blood vessels: assessment of the potential craniovascular selectivity of sumatriptan.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Mar;53(3):266-74. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01536.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11874390 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT1D receptor agonists and human coronary artery reactivity in vitro: crossover comparisons of 5-HT and sumatriptan with rizatriptan and L-741,519.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1996 Oct;42(4):431-41. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1996.04217.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8904614 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the vasoconstrictor effects of the selective 5-HT1D-receptor agonist L-775,606 with the mixed 5-HT1B/1D-receptor agonist sumatriptan and 5-HT in human isolated coronary artery.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;49(2):126-31. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00129.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10671906 Free PMC article.
-
Current and emerging second-generation triptans in acute migraine therapy: a comparative review.J Clin Pharmacol. 2000 Jul;40(7):687-700. doi: 10.1177/00912700022009431. J Clin Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10883409 Review.
-
Migraine pharmacotherapy with oral triptans: a rational approach to clinical management.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000 Mar;1(3):391-404. doi: 10.1517/14656566.1.3.391. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2000. PMID: 11249525 Review.
Cited by
-
Collar-induced elevation of mRNA and functional activity of 5-HT(1B) receptor in the rabbit carotid artery.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Dec;131(8):1723-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703732. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11139452 Free PMC article.
-
Rizatriptan in the treatment of migraine.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006 Sep;2(3):247-59. doi: 10.2147/nedt.2006.2.3.247. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2006. PMID: 19412472 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of migraine attacks based on the interaction with the trigemino-cerebrovascular system.J Headache Pain. 2008 Feb;9(1):5-12. doi: 10.1007/s10194-008-0011-4. Epub 2008 Jan 23. J Headache Pain. 2008. PMID: 18217201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triptans and CGRP blockade - impact on the cranial vasculature.J Headache Pain. 2017 Oct 10;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0811-5. J Headache Pain. 2017. PMID: 29019093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative effects of frovatriptan and sumatriptan on coronary and internal carotid vascular haemodynamics in conscious dogs.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;132(5):1071-83. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703917. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11226138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Humphrey PPA, Feniuk W. Mode of action of the anti-migraine drug sumatriptan. Tr Pharmacol Sci. 1991;12:444–446. - PubMed
-
- Friberg L, Olesen J, Iversen HK, Sperling B. Migraine pain associated with middle cerebral artery dilatation: reversal by sumatriptan. Lancet. 1991;338:13–17. - PubMed
-
- Caekebeke JFV, Ferrari MD, Zetsloot CP, Jansen J, Saxena P. Antimigraine drug sumatriptan increases blood flow velocity in cerebral arteries during migraine attacks. Neurol. 1992;42:1522–1526. - PubMed
-
- Hamel E, Fan E, Linville D, et al. Expression of mRNA for the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine1Dβ receptor subtype in human and bovine cerebral arteries. Mol Pharmacol. 1993;44:242–246. - PubMed
-
- Longmore J, Shaw D, Smith D, et al. Differential distribution of 5-HT1B- and 5-HT1D-immunoreactivity within the human trigemino-cerebrovascular system: implications for the discovery of new anti-migraine drugs. Cephalalgia. 1997;17:833–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

