3-nitroadipate, a metabolic intermediate for mineralization of 2, 4-dinitrophenol by a new strain of a Rhodococcus species
- PMID: 9864324
- PMCID: PMC103543
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.1.149-152.1999
3-nitroadipate, a metabolic intermediate for mineralization of 2, 4-dinitrophenol by a new strain of a Rhodococcus species
Abstract
The bacterial strain RB1 has been isolated by enrichment cultivation with 2,4-dinitrophenol as the sole nitrogen, carbon, and energy source and characterized, on the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence comparison, as a Rhodococcus species closely related to Rhodococcus opacus. Rhodococcus sp. strain RB1 degrades 2,4-dinitrophenol, releasing the two nitro groups from the compound as nitrite. The release of nitro groups from 2,4-dinitrophenol occurs in two steps. First, the 2-nitro group is removed as nitrite, with the production of an aliphatic nitro compound identified by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry as 3-nitroadipate. Then, this metabolic derivative is further metabolized, releasing its nitro group as nitrite. Full nitrite assimilation upon reduction to ammonia requires that an additional carbon source be supplied to the medium.
Figures


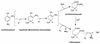
References
-
- Caballero F J, Moreno-Vivián C, Castillo F, Cárdenas J. Nitrite uptake system in photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata E1F1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;848:16–23.
-
- Gottschalk G, Knackmuss H-J. Bacteria and the biodegradation of chemicals achieved naturally, by combination, or by construction. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1993;32:1398–1408.
-
- Gutell R R, Weiser B, Woese C R, Noller H F. Comparative anatomy of 16S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

