Recruitment of ZipA to the septal ring of Escherichia coli is dependent on FtsZ and independent of FtsA
- PMID: 9864327
- PMCID: PMC103546
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.1.167-176.1999
Recruitment of ZipA to the septal ring of Escherichia coli is dependent on FtsZ and independent of FtsA
Abstract
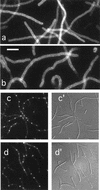
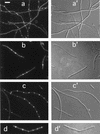
Cell division in prokaryotes is mediated by the septal ring. In Escherichia coli, this organelle consists of several essential division proteins, including FtsZ, FtsA, and ZipA. To gain more insight into how the structure is assembled, we studied the interdependence of FtsZ, FtsA, and ZipA localization using both immunofluorescence and Gfp tagging techniques. To this end, we constructed a set of strains allowing us to determine the cellular location of each of these three proteins in cells from which one of the other two had been specifically depleted. Our results show that ZipA fails to accumulate in a ring shape in the absence of FtsZ. Conversely, depletion of ZipA does not abolish formation of FtsZ rings but leads to a significant reduction in the number of rings per unit of cell mass. In addition, ZipA does not appear to require FtsA for assembly into the septal ring and vice versa. It is suggested that septal ring formation starts by assembly of the FtsZ ring, after which ZipA and FtsA join this structure in a mutually independent fashion through direct interactions with the FtsZ protein.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

