An endoglucanase, EglA, from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus hydrolyzes beta-1,4 bonds in mixed-linkage (1-->3),(1-->4)-beta-D-glucans and cellulose
- PMID: 9864341
- PMCID: PMC103560
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.1.284-290.1999
An endoglucanase, EglA, from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus hydrolyzes beta-1,4 bonds in mixed-linkage (1-->3),(1-->4)-beta-D-glucans and cellulose
Abstract
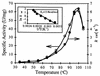
The eglA gene, encoding a thermostable endoglucanase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus, was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The nucleotide sequence of the gene predicts a 319-amino-acid protein with a calculated molecular mass of 35.9 kDa. The endoglucanase has a 19-amino-acid signal peptide but not cellulose-binding domain. The P. furiosus endoglucanase has significant amino acid sequence similarities, including the conserved catalytic nucleophile and proton donor, with endoglucanases from glucosyl hydrolase family 12. The purified recombinant enzyme hydrolyzed beta-1,4 but not beta-1,3 glucosidic linkages and had the highest specific activity on cellopentaose (degree of polymerization [DP] = 5) and cellohexaose (DP = 6) oligosaccharides. To a lesser extent, EglA also hydrolyzed shorter cellodextrins (DP < 5) as well as the amorphous portions of polysaccharides which contain only beta-1,4 bonds such as carboxymethyl cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, Whatman paper, and cotton linter. The highest specific activity toward polysaccharides occurred with mixed-linkage beta-glucans such as barley beta-glucan and lichenan. Kinetics studies with cellooliogsaccharides and p-nitrophenyl-cellooligosaccharides indicated that the enzyme had three glucose binding subsites (-I, -II, and -III) for the nonreducing end and two glucose binding subsites (+I and +II) for the reducing end from the scissile glycosidic linkage. The enzyme had temperature and pH optima of 100 degreesC and 6.0, respectively; a half-life of 40 h at 95 degreesC; and a denaturing temperature of 112 degreesC as determined by differential scanning calorimetry. The discovery of a thermostable enzyme with this substrate specificity has implications for both the evolution of enzymes involved in polysaccharide hydrolysis and the occurrence of growth substrates in hydrothermal vent environments.
Figures


References
-
- Allard B, Tazi A. Influence of growth status on composition of extracellular polysaccharides from two Chlamydomonas species. Phytochemistry. 1993;32:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Anderson M A, Stone B A. New substrate for investigating the specificity of β-glucan hydrolases. FEBS Lett. 1975;52:202–207. - PubMed
-
- Bamforth C W. Barley β-glucans—their role in malting and brewing. Brew Dig. 1982;35:22–27.
-
- Bauer M W, Bylina E, Swanson R, Kelly R M. Comparison of a beat-glucosidase and a beta-mannosidase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus: purification, characterization, gene cloning, and sequence analysis. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:23749–23755. - PubMed
-
- Belton P S, Tanner S F, Cartier N, Chanzy H. High resolution solid-state C-13 nuclear magnetic-resonance spectroscopy of tunicin, an animal cellulose. Macromolecules. 1989;22:1615–1617.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

