In vitro activity of the ketolide HMR 3647 (RU 6647) for Legionella spp., its pharmacokinetics in guinea pigs, and use of the drug to treat guinea pigs with Legionella pneumophila pneumonia
- PMID: 9869571
- PMCID: PMC89026
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.1.90
In vitro activity of the ketolide HMR 3647 (RU 6647) for Legionella spp., its pharmacokinetics in guinea pigs, and use of the drug to treat guinea pigs with Legionella pneumophila pneumonia
Abstract
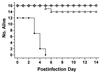
The activities of HMR 3647, HMR 3004, erythromycin, clarithromycin, and levofloxacin for 97 Legionella spp. isolates were determined by microbroth dilution susceptibility testing. Growth inhibition of two Legionella pneumophila strains grown in guinea pig alveolar macrophages was also determined. The concentrations required to inhibit 50% of strains tested were 0.06, 0.02, 0.25, 0.03, and 0.02 microg/ml for HMR 3647, HMR 3004, erythromycin, clarithromycin, and levofloxacin, respectively. BYEalpha broth did not significantly inhibit the activities of the drugs tested, as judged by the susceptibility of the control Staphylococcus aureus strain; however, when Escherichia coli was used as the test strain, levofloxacin activity tested in BYEalpha broth was fourfold lower. HMR 3647, HMR 3004, erythromycin, and clarithromycin (0.25 and 1 microg/ml) reduced bacterial counts of two L. pneumophila strains grown in guinea pig alveolar macrophages by 0.5 to 1 log10, but regrowth occurred over a 2-day period. HMR 3647, erythromycin, and clarithromycin appeared to have equivalent intracellular activities which were solely static in nature. HMR 3004 was more active than all drugs tested except levofloxacin. In contrast, levofloxacin (1 microg/ml) was bactericidal against intracellular L. pneumophila and significantly more active than the other drugs tested. Therapy studies with HMR 3647 and erythromycin were performed in guinea pigs with L. pneumophila pneumonia. When HMR 3647 was given (10 mg/kg of body weight) by the intraperitoneal route to infected guinea pigs, mean peak plasma levels were 1.4 microg/ml at 0.5 h and 1.0 microg/ml at 1 h postinjection. The terminal half-life phase of elimination from plasma was 1.4 h. All 16 L. pneumophila-infected guinea pigs treated with HMR 3647 (10 mg/kg/dose given intraperitoneally once daily) for 5 days survived for 9 days after antimicrobial therapy, as did all 16 guinea pigs treated with the same dose of HMR 3647 given twice daily. Fourteen of 16 erythromycin-treated (30 mg/kg/dose given intraperitoneally twice daily) animals survived, whereas 0 of 12 animals treated with saline survived. HMR 3647 is effective against L. pneumophila in vitro, in infected macrophages, and in a guinea pig model of Legionnaires' disease. HMR 3647 given once daily should be evaluated as a treatment for Legionnaires' disease in humans.
Figures


References
-
- Agouridas C, Bonnefoy A, Chantot J F. Program and abstracts of the 35th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. In vitro antibacterial activity of RU 004, a novel ketolide highly active against respiratory pathogens, abstr. F158; p. 140.
-
- Barry A L, Fuchs P C, Brown S D. In vitro activity of the new ketolide HMR 3004 compared to an azalide and macrolides against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997;16:767–769. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein N, Behr H, Brun Y, Fleurette J. Program and abstracts of the 35th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. In vitro activity of RU 004 on Legionella species, abstr. F166; p. 142.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

