Mediator protein mutations that selectively abolish activated transcription
- PMID: 9874773
- PMCID: PMC15094
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.1.67
Mediator protein mutations that selectively abolish activated transcription
Abstract
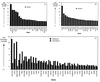
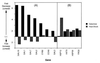
Deletion of any one of three subunits of the yeast Mediator of transcriptional regulation, Med2, Pgd1 (Hrs1), and Sin4, abolished activation by Gal4-VP16 in vitro. By contrast, other Mediator functions, stimulation of basal transcription and of TFIIH kinase activity, were unaffected. A different but overlapping Mediator subunit dependence was found for activation by Gcn4. The genetic requirements for activation in vivo were closely coincident with those in vitro. A whole genome expression profile of a Deltamed2 strain showed diminished transcription of a subset of inducible genes but only minor effects on "basal" transcription. These findings make an important connection between transcriptional activation in vitro and in vivo, and identify Mediator as a "global" transcriptional coactivator.
Figures


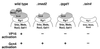
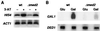
Comment in
-
Transcriptional regulation: contending with complexity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jan 5;96(1):2-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.1.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9874759 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Activator-independent functions of the yeast mediator sin4 complex in preinitiation complex formation and transcription reinitiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(1):349-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.1.349-358.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12482986 Free PMC article.
-
A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II.Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):599-608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90221-6. Cell. 1994. PMID: 8187178
-
Genetic characterization of rbt mutants that enhance basal transcription from core promoters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biochem. 2000 Oct;128(4):575-84. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022789. J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11011139
-
Histone acetyltransferase activity of yeast Gcn5p is required for the activation of target genes in vivo.Genes Dev. 1998 Mar 1;12(5):627-39. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.5.627. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9499399 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator of transcriptional regulation.Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Sep;21(9):335-7. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(96)10051-7. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996. PMID: 8870496 Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal mediator tail subunits contain classical transcriptional activation domains.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;35(8):1363-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01508-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25645928 Free PMC article.
-
Trichoderma reesei XYR1 activates cellulase gene expression via interaction with the Mediator subunit TrGAL11 to recruit RNA polymerase II.PLoS Genet. 2020 Sep 2;16(9):e1008979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008979. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32877410 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cyclic peptide biosynthesis in a plant pathogenic fungus by a novel transcription factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Nov 20;98(24):14174-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.231491298. Epub 2001 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11698648 Free PMC article.
-
KIX domain of AtMed15a, a Mediator subunit of Arabidopsis, is required for its interaction with different proteins.Plant Signal Behav. 2018 Feb 1;13(2):e1428514. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2018.1428514. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Plant Signal Behav. 2018. PMID: 29341856 Free PMC article.
-
Activation domain-mediator interactions promote transcription preinitiation complex assembly on promoter DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 14;100(21):12003-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2035253100. Epub 2003 Sep 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14506297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kelleher R J, III, Flanagan P M, Kornberg R D. Cell. 1990;61:1209–1216. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan P M, Kelleher R J, III, Sayre M H, Tschochner H, Kornberg R D. Nature (London) 1991;350:436–438. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y-J, Bjorklund S, Li Y, Sayre M H, Kornberg R D. Cell. 1994;77:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Koleske A J, Young R A. Nature (London) 1994;368:466–469. - PubMed
-
- Carlson M. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

