Characterization of functionally active subribosomal particles from Thermus aquaticus
- PMID: 9874776
- PMCID: PMC15097
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.1.85
Characterization of functionally active subribosomal particles from Thermus aquaticus
Abstract
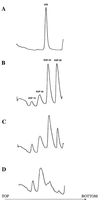
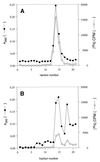
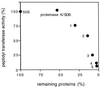
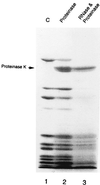
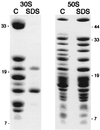
Peptidyl transferase activity of Thermus aquaticus ribosomes is resistant to the removal of a significant number of ribosomal proteins by protease digestion, SDS, and phenol extraction. To define the upper limit for the number of macromolecular components required for peptidyl transferase, particles obtained by extraction of T. aquaticus large ribosomal subunits were isolated and their RNA and protein composition was characterized. Active subribosomal particles contained both 23S and 5S rRNA associated with notable amounts of eight ribosomal proteins. N-terminal sequencing of the proteins identified them as L2, L3, L13, L15, L17, L18, L21, and L22. Ribosomal protein L4, which previously was thought to be essential for the reconstitution of particles active in peptide bond formation, was not found. These findings, together with the results of previous reconstitution experiments, reduce the number of possible essential macromolecular components of the peptidyl transferase center to 23S rRNA and ribosomal proteins L2 and L3. Complete removal of ribosomal proteins from T. aquaticus rRNA resulted in loss of tertiary folding of the particles and inactivation of peptidyl transferase. The accessibility of proteins in active subribosomal particles to proteinase hydrolysis was increased significantly after RNase treatment. These results and the observation that 50S ribosomal subunits exhibited much higher resistance to SDS extraction than 30S subunits are compatible with a proposed structural organization of the 50S subunit involving an RNA "cage" surrounding a core of a subset of ribosomal proteins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reconstitution of functionally active Thermus aquaticus large ribosomal subunits with in vitro-transcribed rRNA.Biochemistry. 1999 Feb 9;38(6):1780-8. doi: 10.1021/bi9822473. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10026258
-
Effect of antibiotics on large ribosomal subunit assembly reveals possible function of 5 S rRNA.J Mol Biol. 1999 Sep 3;291(5):1025-34. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3030. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10518940
-
Unusual resistance of peptidyl transferase to protein extraction procedures.Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1416-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1604315. Science. 1992. PMID: 1604315
-
Histidine 229 in protein L2 is apparently essential for 50S peptidyl transferase activity.Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Nov-Dec;73(11-12):1087-94. doi: 10.1139/o95-117. Biochem Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 8722025 Review.
-
Mechanism of ribosome assisted protein folding: a new insight into rRNA functions.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Jun 26;384(2):137-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.106. Epub 2009 May 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19401192 Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions between 23S rRNA and tRNA in the ribosomal E site.RNA. 2001 Jan;7(1):54-63. doi: 10.1017/s1355838201001650. RNA. 2001. PMID: 11214181 Free PMC article.
-
Which came first: the chicken, the egg, or guanine?RNA. 2023 Sep;29(9):1317-1324. doi: 10.1261/rna.079613.123. Epub 2023 Jun 7. RNA. 2023. PMID: 37286207 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular paleontology: a biochemical model of the ancestral ribosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Mar 1;41(5):3373-85. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt023. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23355613 Free PMC article.
-
UV-induced crosslinks in the 16S rRNAs of Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Thermus aquaticus and their implications for ribosome structure and photochemistry.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Oct 1;28(19):3785-92. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.19.3785. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 11000271 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl-RNA: an evolutionary bridge between RNA and DNA?Chem Biol. 2000 Dec;7(12):R207-16. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(00)00042-9. Chem Biol. 2000. PMID: 11137821 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

