Nuclear endpoint of Wnt signaling: neoplastic transformation induced by transactivating lymphoid-enhancing factor 1
- PMID: 9874785
- PMCID: PMC15106
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.1.139
Nuclear endpoint of Wnt signaling: neoplastic transformation induced by transactivating lymphoid-enhancing factor 1
Abstract
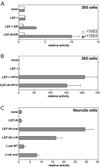
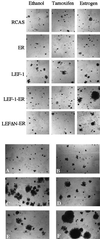
The interaction between beta-catenin and LEF-1/TCF transcription factors plays a pivotal role in the Wnt-1 signaling pathway. The level of beta-catenin is regulated by partner proteins, including glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) and the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor protein. Genetic defects in APC are responsible for a heritable predisposition to colon cancer. APC protein and GSK-3beta bind beta-catenin, retain it in the cytoplasm, and facilitate the proteolytic degradation of beta-catenin. Abrogation of this negative regulation allows beta-catenin to translocate to the nucleus and to form a transcriptional activator complex with the DNA-binding protein lymphoid-enhancing factor 1 (LEF-1). This complex is thought to be involved in tumorigenesis. Here we show that covalent linkage of LEF-1 to beta-catenin and to transcriptional activation domains derived from the estrogen receptor or the herpes simplex virus protein VP16 generates transcriptional regulators that induce oncogenic transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts. The chimeras between LEF-1 and beta-catenin or VP16 are constitutively active, whereas fusions of LEF-1 to the estrogen receptor are regulatable by estrogen. These experiments document the oncogenicity of transactivating LEF-1 and show that the transactivation domain normally provided by beta-catenin can be replaced by heterologous activation domains. These results suggest that the transactivating function of the LEF-1/beta-catenin complex is critical for tumorigenesis and that this complex transforms cells by activating specific LEF-1 target genes.
Figures



References
-
- Cadigan K M, Nusse R. Genes Dev. 1997;11:3286–3305. - PubMed
-
- Morin P J, Sparks A B, Korinek V, Barker N, Clevers H, Vogelstein B, Kinzler K W. Science. 1997;275:1787–1790. - PubMed
-
- Rubinfeld B, Robbins P, El-Gamil M, Albert I, Porfiri E, Polakis P. Science. 1997;275:1790–1792. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R, Varmus H E. Cell. 1982;31:99–109. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R, van Ooyen A, Cox D, Fung Y K, Varmus H. Nature (London) 1984;307:131–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

