Regulation of cadherin function by Rho and Rac: modulation by junction maturation and cellular context
- PMID: 9880323
- PMCID: PMC25150
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.1.9
Regulation of cadherin function by Rho and Rac: modulation by junction maturation and cellular context
Abstract
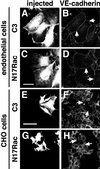
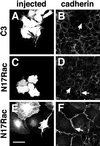
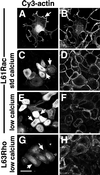
Cadherins are cell-cell adhesion receptors whose adhesive function requires their association with the actin cytoskeleton via proteins called catenins. The small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases), Rho and Rac, are intracellular proteins that regulate the formation of distinct actin structures in different cell types. In keratinocytes and in other epithelial cells, Rho and Rac activities are required for E-cadherin function. Here we show that the regulation of cadherin adhesiveness by the small GTPases is influenced by the maturation status of the junction and the cellular context. E-cadherin localization was disrupted in mature keratinocyte junctions after inhibition of Rho and Rac. However, an incubation of 2 h was required after GTPase inhibition, when compared with newly established E-cadherin contacts (30 min). Regarding other cadherin receptors, P-cadherin was effectively removed from mature keratinocytes junctions by blocking Rho or Rac. In contrast, VE-cadherin localization at endothelial junctions was independent of Rho/Rac activity. We demontrate that the insensitivity of VE-cadherin to inhibition of Rho and Rac was not due to the maturation status of endothelial junction, but rather the cellular background: when transfected into CHO cells, the localization of VE-cadherin was perturbed by inhibition of Rho proteins. Our results suggest that the same stimuli may have different activity in regulating the paracellular activity in endothelial and epithelial cells. In addition, we uncovered possible roles for the small GTPases during the establishment of E-cadherin-dependent contacts. In keratinocytes, Rac activation by itself cannot promote accumulation of actin at the cell periphery in the absence of cadherin-dependent contacts. Moreover, neither Rho nor Rac activation was sufficient to redistribute cadherin molecules to cell borders, indicating that redistribution results mostly from the homophilic binding of the receptors. Our results point out the complexity of the regulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion by the small GTPases, Rho and Rac.
Figures
References
-
- Brady-Kalnay S, Tonks NK. Protein tyrosine phosphatases as cell adhesion receptors. Curr Biol. 1995;7:650–657. - PubMed
-
- Braga VMM, Hodivala KJ, Watt FM. Calcium-induced changes in distribution and solubility of cadherins and their associated cytoplasmic proteins in human keratinocytes. Cell Adhesion Com. 1995;3:201–215. - PubMed
-
- Braga VMM, Najabagheri N, Watt FM. Calcium-induced intercellular adhesion of keratinocytes does not involve accumulation of β1 integrins at cell-cell contact sites and does not involve changes in the levels or phosphorylation of the catenins. Cell Adhesion Com. 1998;5:137–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

