Different tyrosine autophosphorylation requirements in fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 mediate urokinase-type plasminogen activator induction and mitogenesis
- PMID: 9880324
- PMCID: PMC25151
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.1.23
Different tyrosine autophosphorylation requirements in fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 mediate urokinase-type plasminogen activator induction and mitogenesis
Abstract
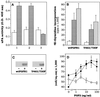
Among the seven tyrosine autophosphorylation sites identified in the intracellular domain of tyrosine kinase fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR1), five of them are dispensable for FGFR1-mediated mitogenic signaling. The possibility of dissociating the mitogenic activity of basic FGF (FGF2) from its urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA)-inducing capacity both at pharmacological and structural levels prompted us to evaluate the role of these autophosphorylation sites in transducing FGF2-mediated uPA upregulation. To this purpose, L6 myoblasts transfected with either wild-type (wt) or various FGFR1 mutants were evaluated for the capacity to upregulate uPA production by FGF2. uPA was induced in cells transfected with wt-FGFR1, FGFR1-Y463F, -Y585F, -Y730F, -Y766F, or -Y583/585F mutants. In contrast, uPA upregulation was prevented in L6 cells transfected with FGFR1-Y463/583/585/730F mutant (FGFR1-4F) or with FGFR1-Y463/583/585/730/766F mutant (FGFR1-5F) that retained instead a full mitogenic response to FGF2; however, preservation of residue Y730 in FGFR1-Y463/583/585F mutant (FGFR1-3F) and FGFR1-Y463/583/585/766F mutant (FGFR1-4Fbis) allows the receptor to transduce uPA upregulation. Wild-type FGFR1, FGFR1-3F, and FGFR1-4F similarly bind to a 90-kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated protein and activate Shc, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)2, and JunD after stimulation with FGF2. These data, together with the capacity of the ERK kinase inhibitor PD 098059 to prevent ERK2 activation and uPA upregulation in wt-FGFR1 cells, suggest that signaling through the Ras/Raf-1/ERK kinase/ERK/JunD pathway is necessary but not sufficient for uPA induction in L6 transfectants. Accordingly, FGF2 was able to stimulate ERK1/2 phosphorylation and cell proliferation, but not uPA upregulation, in L6 cells transfected with the FGFR1-Y463/730F mutant, whereas the FGFR1-Y583/585/730F mutant was fully active. We conclude that different tyrosine autophosphorylation requirements in FGFR1 mediate cell proliferation and uPA upregulation induced by FGF2 in L6 cells. In particular, phosphorylation of either Y463 or Y730, dispensable for mitogenic signaling, represents an absolute requirement for FGF2-mediated uPA induction.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of endothelial cell extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 in urokinase-type plasminogen activator upregulation and in vitro angiogenesis by fibroblast growth factor-2.J Cell Sci. 1999 Aug;112 ( Pt 15):2597-606. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.15.2597. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10393815
-
Differential regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression by basic fibroblast growth factor and serum in myogenesis. Requirement of a common mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jan 23;273(4):2052-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.4.2052. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9442043
-
Biological activity of substrate-bound basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2): recruitment of FGF receptor-1 in endothelial cell adhesion contacts.Oncogene. 2002 May 30;21(24):3889-97. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205407. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12032827
-
[Control of the intracellular signaling induced by fibroblast growth factors (FGF) over the proliferation and survival of retinal pigment epithelium cells: example of the signaling regulation of growth factors endogenous to the retina ].J Soc Biol. 2001;195(2):101-6. J Soc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11723820 Review. French.
-
Deregulation of the signaling pathways controlling urokinase production. Its relationship with the invasive phenotype.Eur J Biochem. 1999 Jul;263(2):295-304. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00507.x. Eur J Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10406935 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of tyrosine residues in constitutively activated fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 involved in mitogenesis, Stat activation, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Apr;12(4):931-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.931. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11294897 Free PMC article.
-
Fibronectin induces endothelial cell migration through β1 integrin and Src-dependent phosphorylation of fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 at tyrosines 653/654 and 766.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7190-202. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304972. Epub 2012 Jan 14. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22247553 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and substrate specificity of the SR protein kinase Clk/Sty.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;23(12):4139-49. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4139-4149.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12773558 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 phosphorylation requirement for cardiomyocyte differentiation in murine embryonic stem cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Aug;13(8A):1489-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00805.x. Epub 2009 Jun 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19549074 Free PMC article.
-
Immunochemical expression of fibroblast growth factor and its receptors in primary tumor cells of renal cell carcinoma.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2021 Feb 15;9(1):65-72. eCollection 2021. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2021. PMID: 33816695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
-
- Basilico C, Moscatelli D. The FGF family of growth factors and oncogenes. Adv Cancer Res. 1992;59:115–165. - PubMed
-
- Bastaki M, Nelli EE, Dell’Era P, Rusnati M, Molinari-Tosatti MP, Parolini S, Auerbach R, Ruco LP, Possati L, Presta M. Basic fibroblast growth factor-induced angiogenic phenotype in mouse endothelium. A study of aortic and microvascular endothelial cell lines. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17:454–464. - PubMed
-
- Besser D, Presta M, Nagamine Y. Elucidation of a signalling pathway induced by FGF-2 leading to uPA gene expression in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1995;6:1009–1017. - PubMed
-
- Blaikie P, Immanuel D, Wu J, Li N, Yajnik V, Margolis B. A region in Shc distinct from the SH2 domain can bind tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:32031–32034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

