Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the JNK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2
- PMID: 9882303
- PMCID: PMC103922
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1023-1035.1999
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the JNK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2
Abstract
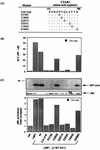
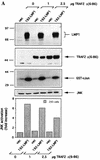
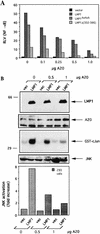
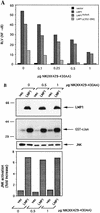
The transforming Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) activates signalling on the NF-kappaB axis through two distinct domains in its cytoplasmic C terminus, namely, CTAR1 (amino acids [aa] 187 to 231) and CTAR2 (aa 351 to 386). The ability of CTAR1 to activate NF-kappaB appears to be attributable to the direct interaction of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), while recent work indicates that CTAR2-induced NF-kappaB is mediated through its association with TNF receptor-associated death domain (TRADD). LMP1 expression also results in activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) (also known as stress-activated protein kinase) cascade, an effect which is mediated exclusively through CTAR2 and can be dissociated from NF-kappaB induction. The organization and signalling components involved in LMP1-induced JNK activation are not known. In this study we have dissected the extreme C terminus of LMP1 and have identified the last 8 aa of the protein (aa 378 to 386) as being important for JNK signalling. Using a series of fine mutants in which single amino acids between codons 379 and 386 were changed to glycine, we have found that mutations of Pro379, Glu381, Ser383, or Tyr384 diminish the ability of LMP1 CTAR2 to engage JNK signalling. Interestingly, this region was also found to be essential for CTAR2-mediated NF-kappaB induction and coincides with the LMP1 amino acid sequences shown to bind TRADD. Furthermore, we have found that LMP1-mediated JNK activation is synergistically augmented by low levels of TRADD expression, suggesting that this adapter protein is critical for LMP1 signalling. TRAF2 is known to associate with TRADD, and expression of a dominant-negative N-terminal deletion TRAF2 mutant was found to partially inhibit LMP1-induced JNK activation in 293 cells. In addition, the TRAF2-interacting protein A20 blocked both LMP1-induced JNK and NF-kappaB activation, further implicating TRAF2 in these phenomena. While expression of a kinase-inactive mutated NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK), a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase which also associates with TRAF2, impaired LMP1 signalling on the NF-kappaB axis, it did not inhibit LMP1-induced JNK activation, suggesting that these two pathways may bifurcate at the level of TRAF2. These data further define a role for TRADD and TRAF2 in JNK activation and confirm that LMP1 utilizes signalling mechanisms used by the TNF receptor/CD40 family to elicit its pleiotropic activities.
Figures






References
-
- Baichwal V R, Sudgen B. Transformation of Balb 3T3 cells by the BNLF1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene. 1988;2:461–467. - PubMed
-
- Brodeur S R, Cheng G, Baltimore D, Thorley-Lawson D A. Localization of the major NF-κB -activating site and the sole TRAF3 binding site of LMP1 defines two distinct signaling motifs. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19777–19784. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel D V. TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature (London) 1996;383:443–446. - PubMed
-
- Cheng G, Baltimore D. TANK, a co-inducer with TRAF2 of TNF- and CD40L-mediated NF-κB activation. Genes Dev. 1996;10:963–973. - PubMed
-
- Dawson C W, Rickinson A B, Young L S. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein inhibits human epithelial cell differentiation. Nature (London) 1990;344:777–780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

