Distinct recognition of non-clade B human immunodeficiency virus type 1 epitopes by cytotoxic T lymphocytes generated from donors infected in Africa
- PMID: 9882385
- PMCID: PMC104004
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.2.1708-1714.1999
Distinct recognition of non-clade B human immunodeficiency virus type 1 epitopes by cytotoxic T lymphocytes generated from donors infected in Africa
Abstract
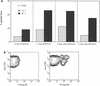
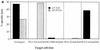
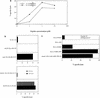
We present detailed studies of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses to clade A or C HIV type 1 in three donors infected in East Africa. We define several novel non-clade B CTL epitopes, including some restricted by HLA alleles common in Africans. Although cross-clade CTL recognition of these epitopes does occur, recognition can also be highly clade specific.
Figures




References
-
- Ada G L, McElrath M J. HIV-1 vaccine-induced cytotoxic T-cell responses: potential role in vaccine efficacy. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1997;13:205–210. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Moss P A H, Goulder P, Barouch D, McHeyzer-Williams M, Bell J I, McMichael A J, Davis M M. Direct visualization and phenotypic analysis of virus-specific T lymphocytes in HIV-infected individuals. Science. 1996;274:94–96.
-
- Bangham C R M, Phillips R E. What is required of an HIV vaccine? Lancet. 1997;350:1617–1621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

